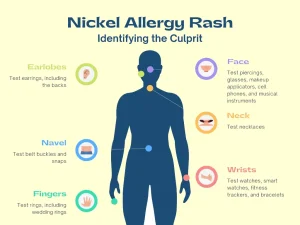
Overview
Nickel allergy is a common form of contact dermatitis that occurs when the skin comes into contact with nickel-containing materials. Nickel is a metal widely used in jewelry, watches, eyeglass frames, coins, buttons, zippers, and electronic devices. In people with a nickel allergy, exposure triggers an immune response that leads to skin inflammation. The condition is not contagious and may develop at any age.
Symptoms
Symptoms of nickel allergy usually appear within hours to days after contact:
-
Redness and inflammation at the site of contact
-
Itching or burning sensation
-
Rash or raised bumps
-
Dry, scaly, or cracked skin
-
Blisters or oozing in more severe reactions
Symptoms typically occur where nickel touches the skin but may spread with repeated exposure.
Causes
Nickel allergy develops when the immune system becomes sensitized to nickel after repeated or prolonged exposure. Once sensitized, even small amounts of nickel can trigger an allergic reaction. The exact reason why some individuals develop sensitivity while others do not is not fully understood.
Risk Factors
Several factors increase the likelihood of developing a nickel allergy:
-
Frequent exposure to nickel-containing jewelry or accessories
-
Body piercings, especially ear piercings
-
Occupational exposure to metals
-
Female sex, partly due to higher jewelry use
-
History of other allergic conditions
The risk increases with prolonged or repeated skin contact.
Complications
If nickel allergy is not properly managed, complications may occur:
-
Chronic or recurrent dermatitis
-
Skin thickening from repeated scratching
-
Secondary bacterial skin infections
-
Sleep disturbance due to persistent itching
-
Reduced quality of life
Avoiding triggers is essential to prevent long-term skin problems.
Prevention
Nickel allergy can often be prevented or managed by minimizing exposure:
-
Avoiding jewelry and accessories containing nickel
-
Choosing hypoallergenic or nickel-free products
-
Using protective coatings on metal items
-
Wearing clothing barriers between skin and metal fasteners
-
Seeking early treatment for persistent skin irritation
Awareness and avoidance of nickel-containing items are key to preventing allergic reactions and reducing symptom severity.
Advertisement