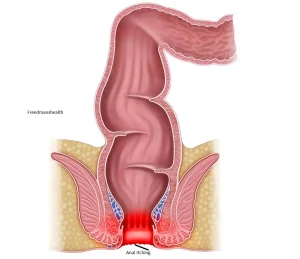
Overview
Anal itching is a common condition that causes an intense urge to scratch the skin in or around the anus. The itching can be uncomfortable, embarrassing and sometimes severe enough to interfere with daily activities or sleep.
Anal itching is also known as pruritus ani. It can have many possible causes, including infections, hemorrhoids and long-lasting diarrhea. Skin irritation or inflammation, also called dermatitis, is another frequent cause.
In many cases, anal itching improves with simple self-care measures. If symptoms persist or worsen, medical evaluation may be needed. With proper treatment, most people experience complete relief.
Symptoms
Symptoms of anal itching can vary depending on the cause and severity. Common symptoms include:
-
Intense itching in or around the anus
-
Redness or inflammation of the anal skin
-
Burning sensation
-
Soreness or discomfort
The itching and irritation may be temporary or ongoing. Symptoms are often worse at night or in warm, humid conditions.
When to see a doctor
Medical care is not always needed, but you should contact a healthcare professional if:
-
Anal itching is severe, persistent or worsening
-
You notice anal bleeding or leakage of stool
-
The anal area appears infected
-
You are unable to identify the cause of ongoing itching
A medical evaluation can help identify underlying conditions and guide effective treatment.
Causes
Anal itching can develop due to a wide range of conditions. In some cases, more than one factor may be involved.
Possible causes include:
-
Skin irritants, such as stool leakage, long-term diarrhea, harsh soaps or excessive wiping
-
Infections, including sexually transmitted infections, pinworm infestation and yeast infections
-
Skin conditions, such as dry skin, psoriasis or contact dermatitis
-
Other medical conditions, including diabetes, thyroid disorders and hemorrhoids
In many people, no specific cause is identified. This is referred to as idiopathic anal itching.
Prevention
Anal itching cannot always be prevented, but certain measures may reduce the risk and help prevent recurrence.
Keeping the anal area clean and dry can help minimize irritation. Gentle cleansing with water and avoiding harsh soaps may protect sensitive skin. Wearing loose, breathable clothing and cotton underwear can reduce moisture buildup.
Managing diarrhea or constipation, avoiding excessive wiping and addressing underlying medical conditions may also help prevent symptoms. If itching recurs frequently, a healthcare professional can provide guidance on long-term management strategies.
Advertisement