Overview
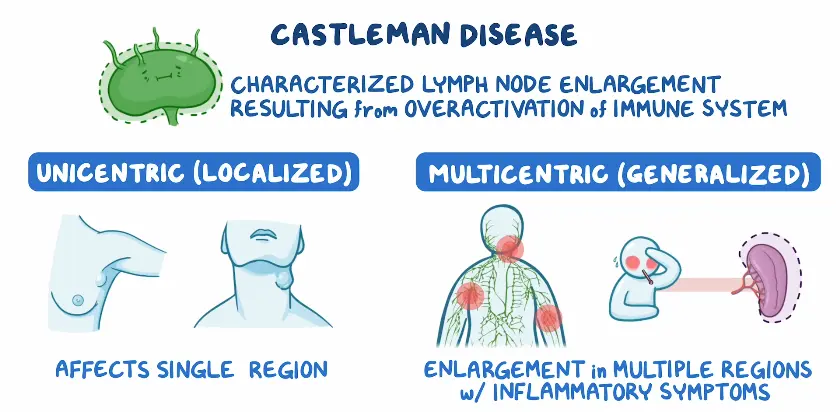
Castleman disease is a rare disorder characterized by abnormal growth of lymph node tissue. It is not a single disease but a group of related conditions that involve an overgrowth of cells in the body’s lymphatic system. Castleman disease can affect a single lymph node region or multiple areas of the body and may lead to immune system dysfunction. The condition ranges from mild to life-threatening, depending on the type and extent of involvement.
Symptoms
Symptoms of Castleman disease vary widely based on whether the condition is localized or affects multiple lymph node regions.
Common symptoms include:
-
Enlarged lymph nodes, often painless
-
Fatigue
-
Fever
-
Night sweats
-
Unexplained weight loss
In more severe or widespread cases, symptoms may include:
-
Loss of appetite
-
Nausea
-
Abdominal fullness due to enlarged organs
-
Shortness of breath
-
Swelling in the legs or abdomen
Some individuals may have no symptoms, and the condition is discovered incidentally.
Causes
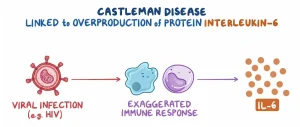
The exact cause of Castleman disease is not fully understood. It involves abnormal immune system activation and excessive production of certain proteins that regulate inflammation and cell growth.
Potential contributing factors include:
-
Immune system dysfunction
-
Overproduction of inflammatory cytokines
-
Viral infections in certain forms of the disease
Different mechanisms are involved depending on the specific subtype of Castleman disease.
Risk Factors
Castleman disease can occur in people of any age, but certain factors may increase risk depending on the form of the condition.
Key risk factors include:
-
Weakened or dysregulated immune system
-
Certain viral infections
-
History of autoimmune or inflammatory conditions
There is no clear genetic inheritance pattern in most cases.
Complications
Castleman disease can lead to serious complications, particularly when multiple lymph node regions are involved.
Possible complications include:
-
Severe infections due to immune system impairment
-
Anemia and other blood disorders
-
Organ dysfunction, including liver or kidney problems
-
Increased risk of certain cancers
-
Life-threatening inflammatory responses
The risk and severity of complications depend on disease type and progression.
Prevention
There is no known way to prevent Castleman disease, but early diagnosis and appropriate management can improve outcomes.
Preventive and protective measures include:
-
Regular medical follow-up for individuals with persistent lymph node enlargement
-
Prompt evaluation of unexplained systemic symptoms
-
Ongoing monitoring to detect complications early
-
Maintaining overall immune health under medical guidance
Early recognition and specialized care are essential in managing Castleman disease and reducing the risk of severe complications.
Advertisement