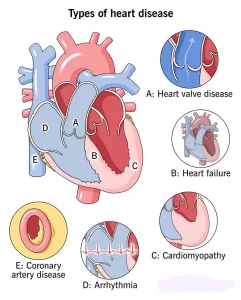
Overview
Heart disease is a broad term that refers to several types of conditions affecting the heart. The most common form is coronary artery disease, which involves narrowing or blockage of the coronary arteries that supply blood to the heart muscle. Other types include heart rhythm problems, heart valve disease, congenital heart defects, and diseases of the heart muscle.
Heart disease often develops slowly over time and may not cause noticeable symptoms in its early stages. As the condition progresses, it can interfere with the heart’s ability to pump blood effectively. Heart disease remains a leading cause of illness and death worldwide, but many forms are preventable with healthy lifestyle choices and proper medical care.
Symptoms
Symptoms of heart disease depend on the specific type and severity of the condition. Some people may not experience symptoms until the disease is advanced.
Common symptoms may include:
-
Chest pain or discomfort
-
Shortness of breath during activity or at rest
-
Fatigue or weakness
-
Irregular heartbeat or palpitations
-
Swelling in the legs, ankles, feet, or abdomen
-
Dizziness or lightheadedness
-
Pain in the neck, jaw, arms, or back
Women, older adults, and people with diabetes may experience less typical symptoms, such as nausea or unexplained fatigue.
Causes
Heart disease can develop due to a variety of underlying problems that affect the heart and blood vessels.
Common causes include:
-
Buildup of fatty deposits in the arteries
-
High blood pressure that strains the heart
-
Damage from heart infections or inflammation
-
Abnormal heart rhythms
-
Structural problems present at birth
-
Long-term damage from diabetes or obesity
Lifestyle factors and genetic predisposition often play a combined role in the development of heart disease.
Risk factors
Certain factors increase the risk of developing heart disease:
-
Increasing age
-
Family history of heart disease
-
Smoking or tobacco use
-
High blood pressure
-
High cholesterol levels
-
Diabetes
-
Obesity
-
Physical inactivity
-
Unhealthy diet
-
Excessive alcohol consumption
-
Chronic stress
The presence of multiple risk factors significantly increases the likelihood of heart disease.
Complications
If left untreated, heart disease can lead to serious and potentially life-threatening complications.
Possible complications include:
-
Heart attack
-
Heart failure
-
Heart arrhythmias
-
Stroke
-
Blood clots
-
Sudden cardiac arrest
-
Reduced quality of life due to physical limitations
Early diagnosis and ongoing management are essential to reduce the risk of complications.
Prevention
Many forms of heart disease can be prevented or delayed by adopting heart-healthy habits and managing existing health conditions.
Prevention strategies include:
-
Eating a nutritious diet low in saturated fat, salt, and added sugars
-
Maintaining a healthy body weight
-
Exercising regularly
-
Quitting smoking and avoiding secondhand smoke
-
Limiting alcohol intake
-
Managing blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar levels
-
Reducing stress through relaxation and healthy coping techniques
-
Taking prescribed medications as directed
-
Scheduling regular medical checkups
Consistent preventive care and lifestyle changes can greatly reduce the risk of heart disease and support long-term heart health.
Advertisement