Overview
Brain arteriovenous malformation is an abnormal connection between arteries and veins in the brain that bypasses the normal capillary system. This disrupts normal blood flow and oxygen delivery to brain tissue. Brain AVMs are often present at birth and may remain undetected for years. However, they can rupture and cause bleeding in the brain, making early diagnosis and proper management important.
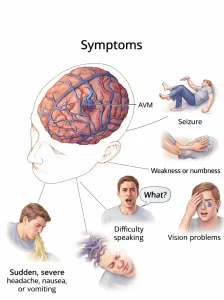
Symptoms
Some people with brain AVM have no symptoms. When symptoms occur, they may vary depending on the size and location of the malformation.
• Headaches that may be severe or persistent
• Seizures
• Weakness or numbness in one part of the body
• Difficulty speaking or understanding speech
• Vision problems
• Loss of balance or coordination
• Sudden severe headache, nausea, or vomiting if bleeding occurs
• Loss of consciousness in severe cases
Causes
The exact cause of brain arteriovenous malformations is not clearly understood.
• Abnormal development of blood vessels during fetal growth
• Congenital defects affecting artery and vein formation
• Rare genetic conditions associated with abnormal blood vessels
Risk factors
Certain factors may increase the risk of having a brain AVM or developing complications.
• Being born with the condition
• Family history of vascular malformations
• Certain inherited disorders such as hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia
• Young age, as symptoms often appear before age 40
Complications
Brain AVMs can lead to serious and potentially life-threatening complications.
• Bleeding in the brain or surrounding tissues
• Stroke due to reduced oxygen supply
• Brain damage affecting movement, speech, or memory
• Chronic headaches or seizures
• Hydrocephalus due to increased pressure in the brain
• Death in severe cases
Prevention
There is no known way to prevent brain arteriovenous malformations, as they typically develop before birth. However, steps can be taken to reduce the risk of complications.
• Regular medical monitoring for diagnosed AVMs
• Managing blood pressure to reduce bleeding risk
• Avoiding smoking and illicit drug use
• Seeking immediate medical attention for sudden neurological symptoms
• Following treatment plans recommended by healthcare professionals
Advertisement