Overview
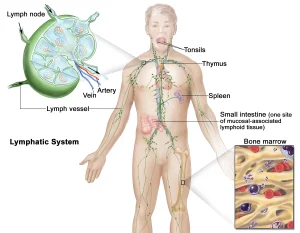
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma is a group of cancers that begin in the lymphatic system, which is part of the body’s immune system. It develops when lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell, grow abnormally and multiply uncontrollably. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma can arise in lymph nodes as well as in other organs such as the spleen, bone marrow, or digestive tract. The disease includes many subtypes that vary in aggressiveness, treatment response, and prognosis.
Symptoms
Symptoms of non-Hodgkin lymphoma can differ depending on the type and extent of the disease:
-
Painless swelling of lymph nodes in the neck, armpits, or groin
-
Persistent fatigue or weakness
-
Fever without infection
-
Night sweats
-
Unexplained weight loss
-
Shortness of breath or cough
-
Abdominal pain or swelling
Some people may have few symptoms in the early stages.
Causes
The exact cause of non-Hodgkin lymphoma is not always known. It occurs when genetic mutations develop in lymphocytes, leading to uncontrolled cell growth. These mutations may be influenced by immune system dysfunction, infections, or environmental exposures. In some cases, viruses or bacteria are linked to specific lymphoma subtypes.
Risk Factors
Several factors increase the risk of developing non-Hodgkin lymphoma:
-
Older age
-
Weakened immune system due to illness or medications
-
Autoimmune diseases
-
Certain viral or bacterial infections
-
Exposure to chemicals such as pesticides or solvents
-
Family history of lymphoma
Risk varies depending on the subtype of lymphoma.
Complications
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma can lead to serious complications:
-
Spread of cancer to bone marrow or other organs
-
Increased susceptibility to infections
-
Anemia or bleeding disorders
-
Side effects from chemotherapy, radiation, or immunotherapy
-
Recurrence of the disease after treatment
Close medical follow-up is essential to manage complications effectively.
Prevention
There is no sure way to prevent non-Hodgkin lymphoma, but some measures may reduce risk:
-
Managing conditions that weaken the immune system
-
Avoiding unnecessary exposure to harmful chemicals
-
Seeking early treatment for chronic infections
-
Maintaining regular medical check-ups
Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment improve outcomes and quality of life for people with non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
Advertisement