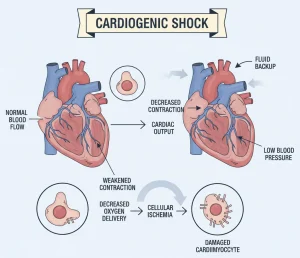
Overview
Cardiogenic shock is a life-threatening condition in which the heart suddenly cannot pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs. This leads to severe reduction in blood flow to vital organs, causing organ failure if not treated immediately. Cardiogenic shock most commonly occurs as a complication of a severe heart attack but can also result from other serious heart conditions.
Symptoms
Symptoms of cardiogenic shock develop rapidly and reflect poor blood circulation and oxygen delivery.
Common symptoms include:
-
Rapid breathing
-
Severe shortness of breath
-
Chest pain
-
Cold, clammy skin
-
Pale or bluish skin color
-
Weak or rapid pulse
Other symptoms may include:
-
Confusion or altered mental status
-
Low blood pressure
-
Decreased urine output
-
Extreme fatigue
-
Loss of consciousness
Causes
Cardiogenic shock occurs when the heart’s pumping ability is severely impaired.
Common causes include:
-
Severe heart attack damaging a large portion of the heart muscle
-
Heart failure
-
Abnormal heart rhythms
-
Rupture of heart structures such as valves or walls
-
Cardiomyopathy
-
Severe heart valve disease
The condition results in inadequate circulation of oxygen-rich blood.
Risk Factors
Certain factors increase the risk of developing cardiogenic shock, especially in individuals with underlying heart disease.
Key risk factors include:
-
History of heart attack
-
Coronary artery disease
-
Advanced age
-
Diabetes
-
High blood pressure
-
Previous heart failure
-
Smoking
People with multiple cardiovascular risk factors are at higher risk.
Complications
Cardiogenic shock can quickly lead to serious and often fatal complications if not treated promptly.
Possible complications include:
-
Multi-organ failure
-
Kidney failure
-
Liver damage
-
Brain injury due to lack of oxygen
-
Cardiac arrest
-
Death
The severity and duration of shock strongly influence outcomes.
Prevention
While cardiogenic shock cannot always be prevented, reducing the risk of heart disease can significantly lower the likelihood of its occurrence.
Preventive measures include:
-
Managing blood pressure, cholesterol, and diabetes
-
Avoiding tobacco use
-
Maintaining a heart-healthy diet
-
Staying physically active
-
Seeking immediate medical care for heart attack symptoms
-
Adhering to prescribed heart medications
Early recognition and rapid treatment of heart conditions are critical to preventing cardiogenic shock and improving survival.
Advertisement