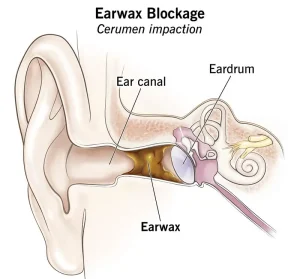
Overview
Earwax blockage, also known as cerumen impaction, occurs when earwax builds up and hardens inside the ear canal. Earwax is a natural substance produced by glands in the ear that helps protect the ear canal by trapping dust, debris, and bacteria. Normally, earwax moves outward on its own and falls out of the ear.
Problems develop when too much earwax accumulates or when it is pushed deeper into the ear canal. This blockage can interfere with hearing and cause discomfort. Earwax blockage is common and can affect people of all ages. In most cases, it can be safely treated with proper care or medical assistance.
Symptoms
Symptoms of earwax blockage depend on how much wax has accumulated and how completely it blocks the ear canal.
Common symptoms include:
-
Partial or sudden hearing loss in the affected ear
-
A feeling of fullness or pressure in the ear
-
Earache or discomfort
-
Ringing in the ear, also known as tinnitus
-
Itching in the ear canal
-
Dizziness in some cases
-
Cough triggered by stimulation of the ear canal
Symptoms may develop gradually and often affect only one ear, though both ears can be involved.
Causes
Earwax blockage usually occurs when earwax is not able to move out of the ear canal naturally. This can happen for several reasons.
Common causes include:
-
Using cotton swabs, hairpins, or other objects that push wax deeper into the ear
-
Wearing hearing aids, earplugs, or earbuds that block natural earwax movement
-
Producing excessive earwax
-
Narrow or hairy ear canals
-
Skin conditions such as eczema that affect the ear canal
-
Age-related changes that cause earwax to become harder and drier
Instead of removing wax, improper cleaning methods often make blockage worse.
Risk factors
Certain factors increase the risk of developing earwax blockage:
-
Older age, as earwax tends to harden over time
-
Regular use of hearing aids or earplugs
-
Habitual use of cotton swabs or similar objects
-
Anatomical differences such as narrow ear canals
-
Conditions that affect skin health in the ear canal
These factors make it more likely for earwax to accumulate and become impacted.
Complications
If earwax blockage is not treated, it can lead to complications, especially when the blockage is severe or long-lasting.
Possible complications include:
-
Ongoing hearing problems
-
Ear pain or infection
-
Damage to the ear canal or eardrum from improper removal attempts
-
Worsening tinnitus
-
Balance problems in rare cases
Seeking proper treatment can help prevent these issues and protect ear health.
Prevention
Earwax blockage can often be prevented with simple ear care habits:
-
Avoid inserting objects into the ear canal, including cotton swabs
-
Clean only the outer part of the ear with a washcloth
-
Use hearing aids and earplugs as directed and clean them regularly
-
Seek medical advice if you have frequent earwax buildup
-
Use earwax-softening drops only if recommended by a healthcare professional
Allowing earwax to follow its natural clearing process is the safest way to prevent blockage.
Advertisement