Overview
Chlamydia trachomatis is a bacterial infection caused by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis. It is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections worldwide and often affects the genital tract, rectum, and eyes. Many infected individuals do not experience noticeable symptoms, which allows the infection to persist and spread unknowingly. If left untreated, chlamydia can lead to serious reproductive and systemic health complications.
Symptoms
Symptoms of Chlamydia trachomatis infection vary by sex and site of infection, and many people remain asymptomatic.
Common symptoms may include:
-
Abnormal vaginal or penile discharge
-
Burning sensation during urination
-
Lower abdominal or pelvic pain
-
Pain during sexual intercourse
-
Rectal pain, discharge, or bleeding
In some cases, additional symptoms may include:
-
Testicular pain or swelling
-
Irregular menstrual bleeding
-
Eye redness or discharge if the eyes are infected
-
Sore throat if transmitted through oral contact
Causes
Chlamydia trachomatis infection is caused by direct transmission of the bacterium through intimate contact.
Major causes include:
-
Unprotected vaginal, anal, or oral sex with an infected partner
-
Transmission from an infected mother to her baby during childbirth
-
Direct contact with infected genital secretions
The bacteria infect mucous membranes and multiply inside host cells, leading to inflammation and tissue damage.
Risk Factors
Certain behaviors and conditions increase the risk of acquiring Chlamydia trachomatis infection.
Key risk factors include:
-
Having multiple sexual partners
-
Inconsistent or incorrect condom use
-
Previous history of sexually transmitted infections
-
Young age, particularly adolescents and young adults
-
Lack of routine sexual health screening
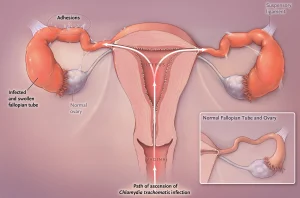
Complications
Untreated Chlamydia trachomatis infection can result in serious and long-term complications.
Potential complications include:
-
Pelvic inflammatory disease
-
Infertility in women
-
Ectopic pregnancy
-
Chronic pelvic pain
-
Epididymitis in men
-
Increased risk of HIV transmission
-
Eye and lung infections in newborns
Early diagnosis and treatment significantly reduce the risk of complications.
Prevention
Chlamydia trachomatis infection is preventable through safe sexual practices and regular screening.
Effective prevention strategies include:
-
Using condoms consistently and correctly
-
Limiting the number of sexual partners
-
Regular sexually transmitted infection testing
-
Prompt treatment of infected individuals and their partners
-
Avoiding sexual contact until treatment is completed
Routine screening and early medical care are essential to preventing the spread and long-term effects of Chlamydia trachomatis infection.
Advertisement