Overview
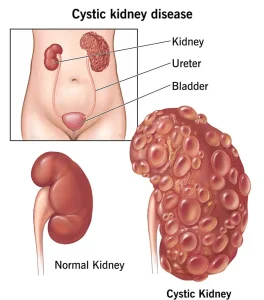
Kidney cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop on or inside the kidneys. They are commonly discovered incidentally during imaging tests done for other medical reasons. Most kidney cysts are noncancerous and harmless, especially simple kidney cysts, which are the most frequent type. In many cases, they do not interfere with kidney function and require no treatment.
Kidney cysts are different from genetic or complex cystic kidney diseases and should not be confused with kidney cancer, although certain complex cysts may need closer evaluation.
Symptoms
Many people with kidney cysts experience no symptoms, particularly when the cysts are small. Symptoms are more likely if a cyst grows large, becomes infected, or ruptures.
Common symptoms may include:
-
Dull pain in the lower back or side
-
Upper abdominal discomfort
-
Fever, if the cyst becomes infected
-
Frequent urination or urinary discomfort
-
Blood in the urine in rare cases
Causes
The exact cause of simple kidney cysts is not fully understood. They may develop when the surface layer of the kidney weakens and forms a pouch that fills with fluid over time.
Possible contributing factors include:
-
Age-related changes in kidney tissue
-
Obstruction of kidney tubules
-
Localized kidney tissue degeneration
Risk Factors
Certain factors increase the likelihood of developing kidney cysts:
-
Increasing age, especially over 50 years
-
Male sex
-
History of kidney disease
-
Long-term kidney dysfunction or dialysis
-
Family history of cystic kidney disorders
Complications
Most kidney cysts do not cause complications. However, in uncommon situations, complications may occur.
Potential complications include:
-
Infection of the cyst, causing fever and pain
-
Rupture of the cyst, leading to sudden discomfort
-
Obstruction of urine flow
-
High blood pressure related to large cysts
-
Reduced kidney function in rare cases
Prevention
There is no guaranteed way to prevent kidney cysts, especially simple cysts that are associated with aging. However, maintaining overall kidney health may reduce the risk of complications.
Preventive measures include:
-
Staying well hydrated
-
Managing blood pressure effectively
-
Avoiding smoking
-
Maintaining a healthy weight
-
Regular medical checkups for those with known kidney conditions
If you want, I can also prepare a section on diagnosis, imaging classification, or treatment options in the same WordPress-ready format.
Advertisement