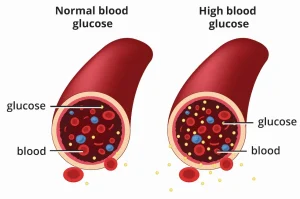
Overview
Diabetes is a chronic metabolic condition characterized by elevated blood glucose levels due to problems with insulin production, insulin action, or both. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose enter cells to be used for energy. When diabetes is not well controlled, it can lead to serious health complications affecting multiple organs. The main types include type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, and gestational diabetes.
Symptoms
Symptoms of diabetes may develop gradually or appear suddenly, depending on the type:
-
Increased thirst
-
Frequent urination
-
Excessive hunger
-
Unexplained weight loss
-
Fatigue or weakness
-
Blurred vision
-
Slow-healing wounds
-
Frequent infections
-
Tingling or numbness in hands or feet
Causes
The causes of diabetes vary by type but involve impaired insulin function:
-
Autoimmune destruction of insulin-producing cells in type 1 diabetes
-
Insulin resistance and reduced insulin production in type 2 diabetes
-
Hormonal changes during pregnancy in gestational diabetes
-
Genetic predisposition
-
Lifestyle factors such as poor diet and physical inactivity
-
Certain medical conditions or medications
Risk Factors
Several factors increase the risk of developing diabetes:
-
Family history of diabetes
-
Overweight or obesity
-
Sedentary lifestyle
-
Unhealthy diet
-
Increasing age
-
High blood pressure or abnormal cholesterol levels
-
History of gestational diabetes
-
Polycystic ovary syndrome
Complications
Poorly controlled diabetes can cause both short-term and long-term complications:
-
Heart disease and stroke
-
Kidney damage
-
Nerve damage
-
Eye problems and vision loss
-
Foot problems and infections
-
Skin conditions
-
Increased risk of infections
-
Sexual and reproductive health issues
Prevention
Some forms of diabetes can be prevented or delayed with healthy lifestyle choices:
-
Maintaining a healthy body weight
-
Eating a balanced, nutrient-rich diet
-
Engaging in regular physical activity
-
Monitoring blood sugar levels when at risk
-
Managing blood pressure and cholesterol
-
Avoiding tobacco use
-
Attending regular health checkups
Advertisement