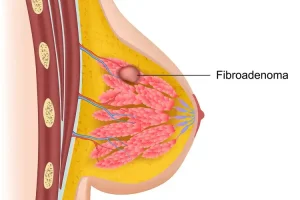
Overview
Fibroadenoma is a common benign breast tumor that usually occurs in young women, particularly between the ages of 15 and 35. It is made up of both glandular and connective breast tissue and is not cancerous. Fibroadenomas often feel like smooth, firm, and rubbery lumps that move easily under the skin. They may remain the same size, shrink, or grow over time and are generally not associated with an increased risk of breast cancer.
Symptoms
Fibroadenomas often do not cause symptoms and are discovered during a breast exam or imaging study. When symptoms are present, they may include:
-
A painless breast lump
-
Smooth, round, or oval shape
-
Firm or rubbery texture
-
Lump that moves easily under the skin
-
Usually affects only one breast, though multiple lumps can occur
Pain or tenderness is uncommon but may occur during hormonal changes.
Causes
The exact cause of fibroadenoma is not fully understood, but hormonal factors, particularly estrogen, are believed to play a role. Fibroadenomas are more likely to develop during reproductive years and may change in size during pregnancy, breastfeeding, or with hormonal therapy.
Risk Factors
Several factors increase the likelihood of developing fibroadenoma:
-
Younger age, especially during adolescence and early adulthood
-
Hormonal changes or fluctuations
-
Use of oral contraceptives at a young age
-
Family history of benign breast disease
Fibroadenomas are less common after menopause unless hormone therapy is used.
Complications
Fibroadenomas are generally harmless, but some complications or concerns may arise:
-
Anxiety or emotional distress related to discovering a breast lump
-
Growth of the lump, leading to discomfort or cosmetic concerns
-
Difficulty distinguishing fibroadenoma from other breast lumps without imaging or biopsy
-
Rare association with complex fibroadenomas that may slightly increase breast cancer risk
Regular monitoring helps ensure accurate diagnosis and management.
Prevention
There is no proven way to prevent fibroadenoma, but maintaining breast health is important:
-
Performing regular breast self-examinations
-
Attending routine clinical breast exams
-
Following recommended breast imaging guidelines
-
Seeking medical evaluation for any new or changing breast lumps
Early assessment and monitoring help manage fibroadenoma effectively and provide reassurance.
Advertisement