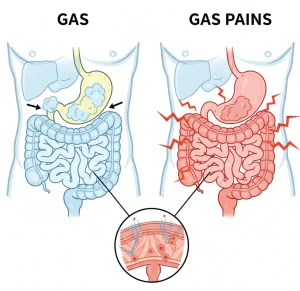
Overview
Gas and gas pains are common digestive issues caused by the buildup of air or gas in the gastrointestinal tract. Gas forms when swallowed air accumulates or when intestinal bacteria break down certain foods during digestion. While passing gas is a normal bodily function, excessive gas or trapped gas can lead to discomfort and pain, affecting daily activities and overall comfort.
Symptoms
Symptoms related to gas and gas pains can vary in intensity and frequency. Common symptoms include:
-
Abdominal bloating or a feeling of fullness
-
Sharp, cramping, or stabbing abdominal pain
-
Pressure or tightness in the abdomen
-
Frequent belching
-
Passing excessive gas
-
Abdominal discomfort that improves after passing gas
Causes
Gas and gas pains occur due to several digestive processes and habits. Common causes include:
-
Swallowing air while eating, drinking, or chewing gum
-
Eating gas-producing foods such as beans, lentils, cabbage, and carbonated drinks
-
Food intolerances, including lactose intolerance
-
Incomplete digestion of certain carbohydrates
-
Digestive disorders that affect normal gut movement
These factors can lead to excess gas production or difficulty moving gas through the intestines.
Risk Factors
Certain factors may increase the likelihood of experiencing gas and gas pains, including:
-
Eating quickly or overeating
-
Consumption of high-fiber or gas-producing foods
-
Use of carbonated beverages
-
Digestive conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome
-
Poor chewing habits
Complications
Gas and gas pains are usually harmless, but ongoing or severe symptoms may indicate underlying digestive problems. Possible complications include:
-
Chronic abdominal discomfort
-
Disruption of daily activities or sleep
-
Anxiety related to persistent digestive symptoms
If gas pains are severe, persistent, or associated with weight loss or bleeding, medical evaluation is important.
Prevention
Gas and gas pains can often be reduced with simple lifestyle changes:
-
Eating slowly and chewing food thoroughly
-
Avoiding known gas-producing foods
-
Limiting carbonated drinks
-
Staying physically active to aid digestion
-
Managing food intolerances with dietary adjustments
Maintaining healthy eating habits can help minimize gas buildup and related discomfort.
Advertisement