Overview
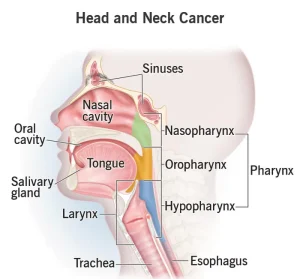
Head and neck cancers are a group of cancers that develop in the tissues of the head and neck region. These cancers most commonly begin in the squamous cells that line the moist surfaces inside the mouth, throat, and voice box. Areas affected may include the lips, mouth, nasal cavity, sinuses, throat, salivary glands, and larynx.
Head and neck cancers are often linked to lifestyle factors such as tobacco and alcohol use, though some cases are associated with viral infections like human papillomavirus. Early diagnosis plays a critical role in successful treatment, as these cancers can affect vital functions such as breathing, speaking, chewing, and swallowing.
Symptoms
Symptoms of head and neck cancers vary depending on the exact location of the cancer. Some symptoms may appear mild at first but persist or worsen over time.
Common symptoms include:
-
A lump or swelling in the neck, jaw, or mouth
-
A sore in the mouth or on the tongue that does not heal
-
Persistent sore throat
-
Difficulty or pain when swallowing
-
Changes in voice, such as hoarseness
-
Ear pain or persistent earache
-
Unexplained weight loss
-
Red or white patches inside the mouth
-
Ongoing nasal congestion or nosebleeds
-
Numbness in the face or mouth
Any symptom that lasts more than a few weeks should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
Causes
Head and neck cancers develop when cells in the head or neck region undergo abnormal changes and begin to grow uncontrollably. These changes are often triggered by long-term exposure to harmful substances or infections.
Major causes include:
-
Tobacco use in any form, including cigarettes, cigars, pipes, chewing tobacco, and snuff
-
Heavy alcohol consumption
-
Combined use of tobacco and alcohol, which greatly increases cancer risk
-
Infection with human papillomavirus, particularly HPV type 16
-
Epstein-Barr virus infection, especially in certain throat and nasal cancers
-
Prolonged exposure to environmental toxins or workplace chemicals
-
Poor oral hygiene and chronic irritation of the mouth
These factors damage the DNA of cells, leading to cancer development over time.
Risk factors
Several factors increase the likelihood of developing head and neck cancers:
-
Use of tobacco products
-
Regular or heavy alcohol intake
-
HPV infection
-
Age over 40 years
-
Male sex
-
Poor nutrition, especially low intake of fruits and vegetables
-
Weakened immune system
-
Long-term sun exposure, particularly for lip cancers
-
Family history of head and neck cancers
Having one or more risk factors does not guarantee cancer, but it significantly raises the risk.
Complications
Head and neck cancers and their treatments can lead to serious complications that affect daily life and overall health.
Possible complications include:
-
Difficulty speaking, chewing, or swallowing
-
Changes in appearance or facial structure
-
Chronic pain
-
Hearing loss
-
Dry mouth and dental problems
-
Breathing difficulties
-
Emotional distress, anxiety, or depression
Rehabilitation and supportive care are often needed to manage these complications and improve quality of life.
Prevention
While not all head and neck cancers can be prevented, certain steps can greatly reduce the risk:
-
Avoiding all forms of tobacco
-
Limiting or avoiding alcohol consumption
-
Practicing safe sex to reduce HPV infection risk
-
Getting vaccinated against HPV when eligible
-
Maintaining good oral hygiene and regular dental checkups
-
Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables
-
Protecting lips and skin from excessive sun exposure
-
Using protective equipment when exposed to workplace chemicals
Early detection through awareness of symptoms and routine medical or dental examinations can also improve outcomes.
Advertisement