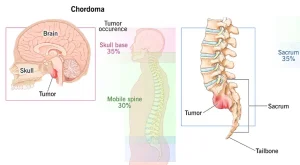
Overview
A vertebral tumor is an abnormal growth that develops in the bones of the spine (vertebrae). These tumors can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous) and may arise from the vertebrae themselves or spread from other parts of the body (metastatic tumors).
Vertebral tumors can affect spinal stability, compress nerves, and impact the spinal cord, potentially causing pain, neurological deficits, or mobility issues. Early detection and treatment are important to prevent complications and preserve quality of life.
Symptoms
Symptoms of vertebral tumors may vary depending on size, location, and whether the tumor is benign or malignant. Common symptoms include:
-
Persistent back or neck pain
-
Pain that worsens at night or during activity
-
Numbness, tingling, or weakness in the arms or legs
-
Difficulty walking or maintaining balance
-
Loss of bladder or bowel control in severe cases
-
Visible or palpable spinal deformity in some cases
-
Fatigue or unexplained weight loss in malignant tumors
Some small vertebral tumors may not cause noticeable symptoms initially.
Causes
Vertebral tumors can arise from various causes depending on their type:
-
Primary bone tumors originating in the vertebrae (e.g., osteosarcoma, chordoma, hemangioma)
-
Metastatic cancer spreading from organs such as the breast, lung, prostate, or kidney
-
Genetic mutations or chromosomal abnormalities
-
Rarely, benign tumors may develop without a clear cause
Risk Factors
Risk factors for vertebral tumors vary by type but may include:
-
Age (certain tumors are more common in children or older adults)
-
Family history of bone cancers
-
History of cancer elsewhere in the body
-
Genetic syndromes that predispose to tumors
-
Exposure to radiation or carcinogenic chemicals
Complications
Untreated vertebral tumors can lead to serious complications:
-
Compression of the spinal cord or nerves, causing paralysis or sensory loss
-
Spinal instability and deformity
-
Chronic or severe pain
-
Loss of bladder or bowel control
-
Metastasis in malignant tumors
-
Reduced mobility and quality of life
Prevention
There is no guaranteed way to prevent vertebral tumors, particularly primary bone cancers. However, steps to reduce risk and detect tumors early include:
-
Regular medical checkups, especially in individuals with a history of cancer
-
Prompt evaluation of persistent or unusual back pain
-
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and avoiding known carcinogens
-
Genetic counseling for individuals with a family history of bone cancers
-
Following recommended cancer screenings to detect metastatic disease early
Early diagnosis and timely treatment, including surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy, significantly improve outcomes for individuals with vertebral tumors.
Advertisement