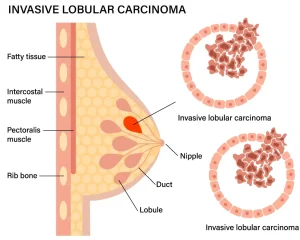
Overview
Invasive lobular carcinoma is a type of breast cancer that begins in the milk-producing lobules of the breast and spreads into surrounding breast tissue. It is the second most common form of invasive breast cancer after invasive ductal carcinoma. Invasive lobular carcinoma often grows in a diffuse pattern, making it harder to detect on physical examination or imaging in its early stages. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are important for improving outcomes.
Symptoms
Symptoms may be subtle and develop gradually. They can include:
-
Thickening or hardening of an area of the breast rather than a distinct lump
-
Change in breast shape or size
-
Breast fullness or swelling
-
Skin changes such as dimpling or indentation
-
Inward turning of the nipple
-
Persistent breast pain or discomfort
-
Swelling in the armpit due to lymph node involvement
Causes
Invasive lobular carcinoma develops when cells in the breast lobules undergo genetic changes that cause uncontrolled growth. These abnormal cells invade nearby breast tissue and may spread to other parts of the body. The exact cause of these genetic mutations is not fully understood, but hormonal influences are believed to play a significant role.
Risk factors
-
Female sex
-
Increasing age
-
Family history of breast cancer
-
Inherited genetic mutations such as BRCA1 or BRCA2
-
Prolonged exposure to estrogen
-
Use of hormone replacement therapy after menopause
-
Personal history of breast cancer or atypical breast changes
Complications
-
Spread of cancer to lymph nodes or distant organs
-
Difficulty in early detection due to diffuse growth pattern
-
Recurrence after treatment
-
Physical and emotional effects related to cancer therapy
-
Treatment-related side effects affecting quality of life
Prevention
While invasive lobular carcinoma cannot always be prevented, risk may be reduced by:
-
Regular breast cancer screening as recommended
-
Performing routine breast self-awareness and reporting changes early
-
Limiting alcohol consumption
-
Maintaining a healthy weight and active lifestyle
-
Discussing risks of hormone therapy with a healthcare provider
-
Genetic counseling and enhanced surveillance for high-risk individuals
Early detection through screening and prompt treatment significantly improve the prognosis for invasive lobular carcinoma.
Advertisement