Overview
Lupus is a chronic autoimmune disease in which the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues throughout the body. It can affect the skin, joints, kidneys, heart, lungs, brain, and blood cells. The most common form is systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus often develops in women of childbearing age and may range from mild to life-threatening. Symptoms typically occur in cycles of flare-ups and remission.
Symptoms
Symptoms of lupus vary widely depending on the organs involved:
-
Fatigue
-
Joint pain, stiffness, and swelling
-
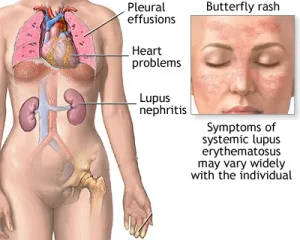
Skin rashes, including a butterfly-shaped rash across the cheeks and nose
-
Sensitivity to sunlight
-
Fever without infection
-
Hair loss
-
Chest pain with deep breathing
-
Mouth sores
-
Swelling in the legs or around the eyes
Symptoms may worsen during flare-ups and improve during remission periods.
Causes
The exact cause of lupus is not fully understood. It is believed to result from a combination of genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors. Potential triggers include:
-
Genetic predisposition
-
Hormonal influences, particularly estrogen
-
Sunlight exposure
-
Infections
-
Certain medications
-
Severe stress
These factors may activate the immune system abnormally in susceptible individuals.
Risk Factors
Factors that increase the likelihood of developing lupus include:
-
Female sex
-
Age between 15 and 45 years
-
Family history of autoimmune disease
-
Certain ethnic backgrounds
-
Exposure to sunlight or specific medications
Risk is influenced by both genetic and environmental elements.
Complications
Lupus can lead to serious complications affecting multiple organs:
-
Kidney damage
-
Cardiovascular disease
-
Lung inflammation
-
Blood clotting disorders
-
Neurological problems
-
Increased risk of infections
-
Pregnancy complications
Early diagnosis and ongoing treatment help reduce the risk of severe outcomes.
Prevention
There is no known way to prevent lupus, but flare-ups may be minimized:
-
Avoiding excessive sun exposure
-
Using sun protection regularly
-
Managing stress
-
Taking prescribed medications consistently
-
Maintaining regular medical follow-up
-
Adopting a healthy lifestyle
Proper management and early treatment are essential for controlling lupus and maintaining quality of life.
Advertisement