Overview
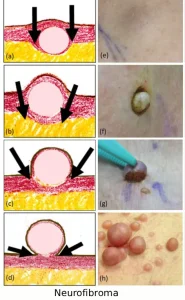
Neurofibroma is a benign tumor that develops from nerve tissue and is made up of a mixture of nerve cells, connective tissue, and supporting cells. These tumors commonly occur on or under the skin but may also develop along deeper nerves in the body. Neurofibromas can appear as isolated growths or as part of a genetic condition known as neurofibromatosis. While most neurofibromas are noncancerous, they may cause symptoms depending on their size and location.
Symptoms
Symptoms of neurofibroma vary based on where the tumor forms and how large it becomes:
-
Soft or firm lumps on or under the skin
-
Skin-colored or slightly pigmented bumps
-
Pain or tenderness if the tumor presses on nearby nerves
-
Tingling, numbness, or weakness in the affected area
-
Cosmetic concerns due to visible growths
Many neurofibromas cause no symptoms and are discovered incidentally.
Causes
Neurofibromas develop due to abnormal growth of cells that surround and support nerves. In people with neurofibromatosis, genetic mutations affect tumor-suppressing genes, leading to multiple tumor growths. Sporadic neurofibromas may occur without a clear inherited cause. The exact trigger for these growths is not always known.
Risk Factors
Several factors increase the likelihood of developing neurofibroma:
-
Neurofibromatosis type 1 or type 2
-
Family history of neurofibromatosis
-
Genetic mutations affecting nerve cell growth
-
Increasing age, as tumors may become more noticeable over time
Risk is higher in individuals with inherited forms of the condition.
Complications
Although neurofibromas are usually benign, complications can occur:
-
Chronic pain due to nerve compression
-
Nerve damage leading to weakness or sensory changes
-
Disfigurement from large or multiple tumors
-
Rare transformation into malignant nerve sheath tumors
-
Emotional or psychological distress
Monitoring is important to detect changes that may signal complications.
Prevention
There is no known way to prevent neurofibroma, especially when it is genetically inherited. However, certain steps may help reduce complications:
-
Regular medical follow-up for individuals with neurofibromatosis
-
Monitoring tumors for changes in size, pain, or appearance
-
Early evaluation of new or rapidly growing lumps
-
Genetic counseling for affected individuals and families
Early detection and ongoing care help manage symptoms and reduce the risk of serious complications associated with neurofibroma.
Advertisement