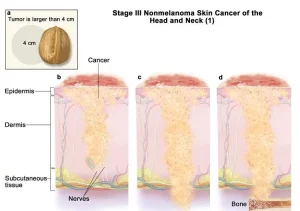
Overview
Nonmelanoma skin cancer refers to a group of skin cancers that develop from cells other than melanocytes, most commonly basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. These cancers typically arise on sun-exposed areas of the body, such as the face, ears, neck, scalp, and hands. Nonmelanoma skin cancers are the most common cancers worldwide and usually grow slowly. With early detection and treatment, they are highly curable.
Symptoms
Symptoms of nonmelanoma skin cancer vary depending on the type and location of the tumor:
-
A persistent, non-healing sore
-
A pearly or waxy bump on the skin
-
A flat, scaly, or crusted patch
-
A firm, red nodule
-
A lesion that bleeds, oozes, or crusts repeatedly
-
A growth with raised edges or a central depression
Any skin change that persists for several weeks should be evaluated.
Causes
Nonmelanoma skin cancer is mainly caused by long-term exposure to ultraviolet radiation from sunlight or tanning devices. UV radiation damages the DNA of skin cells, leading to abnormal cell growth. Over time, repeated sun damage increases the likelihood of cancer development.
Risk Factors
Several factors increase the risk of nonmelanoma skin cancer:
-
Prolonged or intense sun exposure
-
History of sunburns, especially in childhood
-
Fair skin, light hair, and light eyes
-
Older age
-
Weakened immune system
-
Use of tanning beds
-
Previous history of skin cancer
Risk increases with cumulative UV exposure over time.
Complications
Although nonmelanoma skin cancers are usually not life-threatening, complications can occur:
-
Local tissue destruction if untreated
-
Scarring or disfigurement after treatment
-
Recurrence of skin cancer
-
Spread to nearby tissues or lymph nodes in rare cases
-
Increased risk of developing additional skin cancers
Regular skin examinations help reduce the risk of complications.
Prevention
Nonmelanoma skin cancer can often be prevented by protecting the skin from UV exposure:
-
Using broad-spectrum sunscreen daily
-
Wearing protective clothing, hats, and sunglasses
-
Avoiding peak sun hours
-
Staying away from tanning beds
-
Performing regular self-skin examinations
-
Scheduling routine skin checks with a healthcare provider
Consistent sun protection and early detection are key to reducing the risk and impact of nonmelanoma skin cancer.
Advertisement