Overview
Roseola is a common viral infection that primarily affects infants and young children, usually between 6 months and 2 years of age. It is most often caused by human herpesvirus 6 and, less commonly, human herpesvirus 7. Roseola is characterized by a sudden high fever followed by the appearance of a distinctive rash as the fever subsides. The illness is generally mild and resolves on its own.
Symptoms of Roseola
Symptoms typically develop suddenly and follow a characteristic pattern.
-
Sudden high fever lasting several days
-
Irritability or fussiness
-
Mild upper respiratory symptoms such as runny nose or cough
-
Decreased appetite
-
Swollen lymph nodes in the neck
-
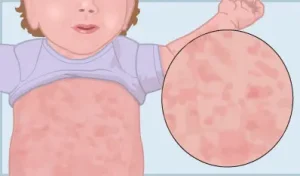
Rash appearing after the fever breaks, starting on the trunk and spreading to the neck and limbs
The rash is usually pink, flat or slightly raised, and not itchy.
Causes of Roseola
Roseola is caused by viral infection, most commonly human herpesvirus 6.
Key points include:
-
Spread through respiratory droplets or saliva
-
Incubation period of about 5 to 15 days
-
Common exposure in early childhood
Once infected, most children develop lasting immunity.
Risk Factors for Roseola
Certain factors increase the likelihood of developing roseola.
-
Age under 2 years
-
Close contact with infected individuals
-
Exposure in daycare or group childcare settings
-
Immature immune system in infants
Complications of Roseola
Roseola is usually mild, but complications can occur, particularly during the fever phase.
-
Febrile seizures due to sudden high fever
-
Dehydration from reduced fluid intake
-
Rare neurological complications in severe cases
Most children recover fully without long-term effects.
Prevention of Roseola
There is no vaccine specifically for roseola, but general preventive measures can reduce spread.
-
Frequent handwashing
-
Avoiding close contact with infected individuals when possible
-
Maintaining good hygiene in childcare environments
-
Monitoring infants for high fever and seeking medical care if seizures occur
Supportive care and fever management are usually sufficient for recovery from roseola.
Advertisement