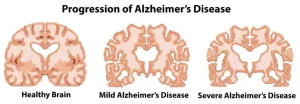
Overview
Diagnosis
Diagnosing Alzheimer’s disease involves several steps:
-
Medical history and physical exam
-
Cognitive and neurological tests
-
Blood tests to rule out other causes of dementia
-
Brain imaging such as MRI or CT scans to detect changes in brain structure
Early diagnosis is important to slow disease progression and improve quality of life.
Treatment and Management
There is currently no cure for Alzheimer’s disease, but treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life:
-
Medications: Drugs like cholinesterase inhibitors and memantine may help with memory and thinking
-
Lifestyle changes: Regular exercise, healthy diet, mental stimulation, and social engagement can support brain health
-
Supportive care: Counseling, occupational therapy, and caregiver support are essential
-
Clinical trials: Experimental therapies may be available for eligible patients
Prevention and Risk Reduction
While Alzheimer’s disease cannot be completely prevented, certain strategies may lower risk or delay onset:
-
Maintain a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
-
Engage in regular physical activity
-
Keep the brain active with reading, puzzles, or learning new skills
-
Manage cardiovascular health and chronic conditions
-
Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
Advertisement