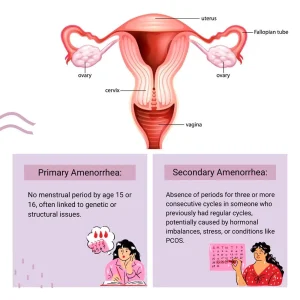
Overview
Diagnosis of Amenorrhea
During your appointment, your doctor will perform a pelvic exam to check for problems with the reproductive organs. If you have never had a period, your doctor may examine your breasts and genitals to evaluate the normal changes of puberty.
Amenorrhea may indicate hormonal imbalances, and identifying the underlying cause often requires multiple tests.
Blood Tests
Several blood tests can help determine the cause of amenorrhea:
-
Pregnancy test: Often the first step to rule out or confirm pregnancy.
-
Thyroid function test: Measures thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) to assess thyroid function.
-
Ovary function test: Measures follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) to evaluate ovarian activity.
-
Prolactin test: Low or high prolactin levels may indicate a pituitary gland issue.
-
Male hormone test: Checks for elevated androgen levels if there are signs such as increased facial hair or deepened voice.
Hormone challenge test
-
You take a hormone medication for 7–10 days to trigger menstrual bleeding.
-
Results help determine if amenorrhea is due to low estrogen levels.
Imaging Tests
Depending on symptoms and blood test results, your doctor may recommend:
-
Ultrasound: Uses sound waves to examine reproductive organs for structural abnormalities.
-
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): Provides detailed images of soft tissues and can detect pituitary tumors.
Scope Tests
-
Hysteroscopy: A thin, lighted camera is inserted through the vagina and cervix to inspect the inside of the uterus.
-
This test is usually done if other tests do not reveal a clear cause.
Treatment of Amenorrhea
Treatment depends on the underlying cause of amenorrhea:
-
Hormone therapy: Birth control pills or other hormone medications can help restart menstrual cycles.
-
Thyroid or pituitary disorders: May require specific medications to correct hormonal imbalances.
-
Structural causes or tumors: Surgery may be necessary to remove blockages or tumors affecting menstrual cycles.
Early diagnosis and treatment can improve reproductive health and overall well-being.
Advertisement