Overview
Diagnosis of Anaphylaxis
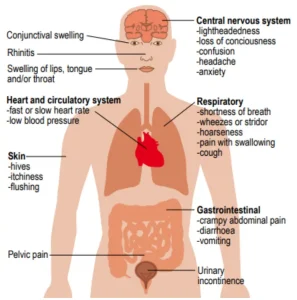
Anaphylaxis is a severe, life-threatening allergic reaction. Diagnosis is often clinical and urgent:
-
Medical history: Rapid onset of symptoms after allergen exposure, such as foods, insect stings, medications, or latex.
-
Symptoms assessment: Involves skin reactions (hives, flushing), airway constriction, low blood pressure, and gastrointestinal symptoms.
-
Emergency recognition: Diagnosis is based on sudden onset, multi-system involvement, and rapid progression.
Treatment of Anaphylaxis
Immediate treatment is critical:
-
Epinephrine: First-line treatment, usually via auto-injector (EpiPen, Auvi-Q).
-
Supportive care: Oxygen, intravenous fluids, and airway management in severe cases.
-
Antihistamines and corticosteroids: Help relieve symptoms but do not replace epinephrine.
-
Allergen avoidance: Long-term management involves identifying and avoiding triggers.
Key Takeaways
-
Anaphylaxis is a medical emergency requiring immediate epinephrine.
-
Recognizing early symptoms is vital for survival.
-
Long-term management includes trigger avoidance and emergency action planning.
Advertisement