Overview
Diagnosis
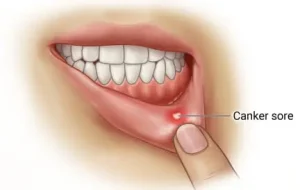
Diagnosis of canker sores is usually based on a visual examination of the mouth by a healthcare professional. Most cases are easily identified because of their characteristic round or oval shape with a white or yellow center and a red border.
In some cases, if sores are severe, frequent, or persistent, additional tests may be needed to rule out other underlying conditions such as:
-
Blood tests to check for vitamin deficiencies or immune system disorders
-
Swab test to rule out viral, bacterial, or fungal infections
-
Biopsy in rare cases to examine tissue under a microscope and exclude other oral diseases
Treatment
Canker sores often heal on their own within one to two weeks without treatment. However, certain therapies can help relieve pain, speed up healing, and prevent recurrence.
Common treatment options include:
-
Topical products such as mouth gels, creams, or ointments containing ingredients like benzocaine or hydrogen peroxide to reduce pain and inflammation
-
Mouth rinses containing corticosteroids or antiseptic agents to ease discomfort and promote healing
-
Oral medications such as corticosteroids for severe or recurrent cases
-
Nutritional supplements like vitamin B12, folate, or iron if deficiencies are the cause
-
Avoiding spicy, acidic, or abrasive foods that can irritate the sore
-
Maintaining good oral hygiene by brushing gently and using a soft toothbrush
-
Using stress management techniques to reduce outbreaks triggered by emotional stress
Prevention
Although canker sores cannot always be prevented, several measures can reduce the frequency and severity of outbreaks.
Preventive steps include:
-
Avoiding foods that trigger mouth irritation, such as citrus fruits or spicy dishes
-
Using toothpaste and mouthwash free from sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS)
-
Eating a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals
-
Managing stress through relaxation techniques like meditation or yoga
-
Protecting the inside of the mouth from injury by avoiding hard or sharp foods
Key Takeaway
Canker sores are small, painful ulcers that form inside the mouth but are not contagious. They usually heal naturally within a short time. Practicing good oral hygiene, managing stress, and avoiding irritants can help prevent frequent flare-ups and promote overall oral health.
Advertisement