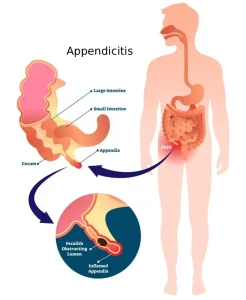
Overview
Diagnosis of Appendicitis
To help diagnose appendicitis, a healthcare professional will take a medical history and carefully examine the abdomen. Several tests may be used to confirm the diagnosis.
-
Physical exam: Gentle pressure is applied to the painful area. When the pressure is suddenly released, appendicitis pain often worsens due to inflammation of the peritoneum. Guarding (involuntary tensing of the abdominal muscles) is another sign.
-
Rectal and pelvic exams: A digital rectal exam may be performed to assess the lower rectum. For individuals of childbearing age, a pelvic exam helps rule out other causes of pain.
-
Blood test: A high white blood cell count may indicate infection.
-
Urine test (urinalysis): Helps rule out urinary tract infections or kidney stones.
-
Imaging tests: Imaging such as abdominal X-ray, ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI may help confirm appendicitis or identify other conditions.
Treatment of Appendicitis
Treatment for appendicitis usually involves surgery to remove the appendix. Before surgery, antibiotics may be given to treat or prevent infection.
Surgery to Remove the Appendix
Appendectomy is the standard surgical procedure to remove the appendix.
-
Open appendectomy (laparotomy): Performed through a single abdominal incision of about 2 to 4 inches.
-
Laparoscopic appendectomy: Uses a few small incisions, a camera, and surgical instruments to remove the appendix.
Laparoscopic surgery generally allows faster recovery, less pain, and minimal scarring. However, open surgery may be required if the appendix has ruptured or if an abscess has formed.
Most patients stay in the hospital for 1 to 2 days after surgery.
Draining an Abscess Before Surgery
If the appendix has burst and an abscess has formed, the abscess may need to be drained first.
-
A drainage tube is inserted through the skin into the abscess.
-
Surgery to remove the appendix is done after the infection is under control.
Non-Surgical Treatment
In mild cases of appendicitis, antibiotic therapy alone may be used to treat the infection. However, if the appendix is not removed, there is a higher chance of appendicitis returning in the future.
Advertisement