Overview
Diagnosis
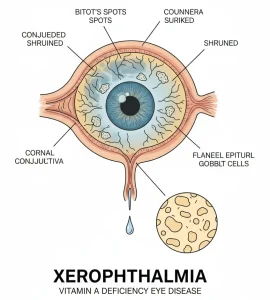
Xerophthalmia is diagnosed through an eye examination and medical history. An ophthalmologist looks for signs of dryness, foamy spots on the conjunctiva (Bitot’s spots), and corneal ulcers. The condition is strongly associated with vitamin A deficiency, so blood tests measuring serum vitamin A levels may be done to confirm the diagnosis. In children, additional evaluation for malnutrition and other vitamin deficiencies may also be recommended.
Treatment
Treatment for xerophthalmia aims to restore normal vitamin A levels and protect the eyes from further damage. This includes:
-
High-dose vitamin A supplementation according to WHO guidelines
-
Dietary improvements with foods rich in vitamin A such as leafy greens, carrots, and liver
-
Managing underlying infections or malnutrition
If corneal ulcers or severe dryness are present, antibiotic eye drops and artificial tears may be prescribed. In advanced cases, corneal transplantation might be needed to restore vision.
Advertisement