Overview
Diagnosis
Ventricular fibrillation is always diagnosed in an emergency situation. When sudden cardiac death occurs, checking for a pulse will show that there is none. Immediate medical attention is essential.
Tests that help diagnose and determine the cause of ventricular fibrillation include:
-
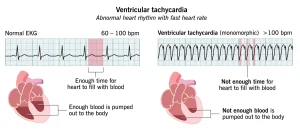
Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG): This test measures the electrical activity of the heart. Electrodes are placed on the chest, arms, and legs to record heart rhythms. During ventricular fibrillation, the ECG typically shows a heartbeat of about 300 to 400 beats per minute.
-
Blood tests: These are done to check for proteins that enter the bloodstream when the heart is damaged, such as during a heart attack.
-
Chest X-ray: This imaging test shows the size and shape of the heart and its blood vessels.
-
Echocardiogram: This test uses sound waves to produce images of the heart in motion, showing the heart’s size, structure, and function.
-
Coronary catheterization (angiogram): A catheter is inserted through a blood vessel, usually in the groin or wrist, and guided to the heart. Dye is injected to make the arteries visible on X-ray images, helping detect blockages.
-
Cardiac computerized tomography (CT): This scan uses X-rays to create detailed cross-sectional images of the heart.
-
Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): This test uses a magnetic field and radio waves to create clear images of the heart and blood flow patterns.
Treatment
Ventricular fibrillation is a life-threatening emergency that requires immediate medical treatment to restore blood flow and prevent brain and organ damage.
Emergency treatment includes:
-
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR): CPR helps maintain blood flow by manually pumping the chest. Push hard and fast at a rate of 100 to 120 compressions per minute, allowing the chest to rise fully between compressions. Continue until an automated external defibrillator (AED) or emergency help arrives.
-
Defibrillation: Also called cardioversion, this treatment delivers electric shocks to the heart using an AED. The device can detect ventricular fibrillation and administer shocks automatically to restore normal rhythm.
After emergency treatment, additional care is provided to prevent future episodes and manage arrhythmia risks.
Medications
Drugs called anti-arrhythmics may be prescribed to control or prevent irregular heart rhythms. These medications help stabilize the heartbeat and reduce the risk of sudden cardiac death.
Surgery or other procedures
Several medical procedures can help manage ventricular fibrillation and its underlying causes:
-
Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD): This small, battery-powered device is implanted under the skin near the collarbone. It continuously monitors heart rhythm and automatically delivers shocks to correct dangerous arrhythmias.
-
Cardiac ablation: This procedure creates tiny scars in the heart using heat or cold energy to block abnormal electrical signals. It’s often performed with thin catheters inserted through blood vessels.
-
Coronary angioplasty and stent placement: If a heart attack caused the condition, a balloon catheter is used to open a blocked artery, and a stent is placed to keep it open and improve blood flow.
-
Coronary bypass surgery: This open-heart surgery reroutes blood around blocked arteries using a healthy blood vessel from another part of the body, improving heart blood flow and reducing the risk of future episodes.
Advertisement