Overview
Diagnosis of Bags Under Eyes
Bags under the eyes are usually noticeable without medical testing. A healthcare professional can evaluate the skin and underlying structures to determine possible causes or to discuss cosmetic or surgical options:
-
Visual examination: Assessment of under-eye skin for puffiness, fat pads, or sagging.
-
Review of contributing factors: Lifestyle, aging, allergies, fluid retention, or genetic predisposition may be considered.
-
Medical assessment: In cases where swelling may indicate a medical condition, further evaluation may be recommended.
Treatment of Bags Under Eyes
Treatment for under-eye bags typically depends on whether the concern is cosmetic or related to an underlying condition:
-
Home and lifestyle measures: Adequate sleep, reducing salt intake, managing allergies, and cold compresses may help reduce puffiness.
-
Medications: Prescription allergy medications may be used if swelling is caused by allergies.
-
Non-surgical therapies: Laser resurfacing, chemical peels, and dermal fillers can improve skin tone, tighten the area, and rejuvenate under-eye appearance. Patients with darker skin should discuss laser risks such as permanent color changes with their healthcare provider.
-
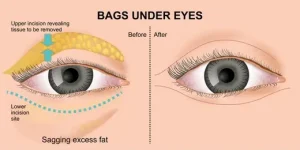
Eyelid surgery (blepharoplasty): Surgical options remove excess fat and skin to correct under-eye bags and improve eyelid appearance. The procedure is usually performed in an outpatient setting using local anesthesia and may address:
-
Baggy or puffy upper eyelids
-
Excess upper eyelid skin affecting vision
-
Droopy lower eyelids exposing the sclera
-
Excess skin on lower eyelids
-
Potential side effects of blepharoplasty include temporary dry eyes, swelling, bruising, pain, and blurred vision. Rare complications can include infection, bleeding, injury to eye muscles, corneal abrasion, eyelid drooping, or vision loss.
Advertisement