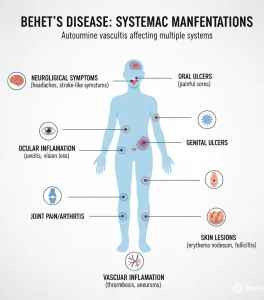
Overview
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of Behcet disease relies on your symptoms, medical history, and sometimes specialized tests. Key factors include:
-
Recurring mouth sores: Painful mouth ulcers appearing at least three times within 12 months are a major diagnostic criterion.
-
Additional symptoms: At least two of the following are generally required for diagnosis:
-
Recurrent genital sores
-
Eye inflammation causing redness or pain
-
Skin lesions
-
Tests to support diagnosis:
-
Lab tests: Blood or other laboratory tests can help rule out similar conditions.
-
Pathergy test: A sterile needle is inserted into the skin and observed for 1–2 days. A small bump at the injection site indicates an overactive immune response.
Treatment
There is no cure for Behcet disease. Treatment focuses on reducing inflammation, managing pain, and preventing complications. Therapy is tailored depending on the severity of symptoms and which parts of the body are affected.
Symptom-Specific Treatments
-
Skin and genital sores: Topical corticosteroid creams, gels, or ointments reduce inflammation and discomfort.
-
Mouth ulcers: Corticosteroid mouth rinses help relieve pain and promote healing.
-
Eye inflammation: Corticosteroid eye drops may reduce mild swelling and irritation.
Systemic Treatments
For more severe or recurrent symptoms, oral medications may be prescribed:
-
Colchicine: Helps prevent recurrent mouth and genital sores and reduces joint swelling.
-
Apremilast: FDA-approved for mouth ulcers caused by Behcet disease. Possible side effects include weight loss and depression.
Treatments for Severe Disease
If Behcet disease affects multiple organs or is persistent, healthcare professionals may prescribe:
-
Corticosteroids: Oral or intravenous steroids like prednisone help control inflammation. Side effects include weight gain, high blood pressure, heartburn, and osteoporosis.
-
Immunosuppressants: Medications such as azathioprine, cyclosporine, or cyclophosphamide reduce immune system activity. These drugs can increase infection risk and affect liver, kidney, and blood health.
-
Immune-modifying agents: Interferon alfa-2b can help manage skin, joint, and eye symptoms. Side effects include flu-like symptoms such as fatigue and muscle aches.
-
TNF inhibitors: Medications like infliximab and adalimumab are used for treatment-resistant or severe Behcet disease. Side effects may include headaches, skin rashes, and increased infection risk.
Advertisement