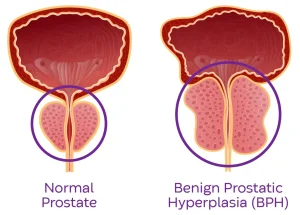
Overview
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of BPH typically starts with a medical history review and a physical exam, including:
-
Digital Rectal Exam (DRE): To check prostate size and texture.
-
Urine Test: Screens for infections or other conditions with similar symptoms.
-
Blood Test: Evaluates kidney function and may include prostate-specific antigen (PSA) to assess prostate health.
Additional tests may include:
-
Urinary Flow Test: Measures strength and volume of urine flow.
-
Postvoid Residual Volume Test: Determines how completely the bladder empties.
-
24-hour Voiding Diary: Tracks urination patterns, especially nighttime urine output.
-
Transrectal Ultrasound (TRUS): Uses sound waves to measure prostate size.
-
Prostate Biopsy: Samples tissue to rule out cancer.
-
Urodynamic and Pressure Flow Studies: Measures bladder muscle function.
-
Cystoscopy: Uses a lighted scope to examine the urethra and bladder.
Treatment
Treatment depends on prostate size, symptoms, overall health, and personal preference. Mild symptoms may not require immediate treatment.
1. Medications
-
Alpha Blockers: Relax bladder and prostate muscles to improve urine flow (e.g., tamsulosin, alfuzosin). Side effects may include dizziness and retrograde ejaculation.
-
5-Alpha Reductase Inhibitors: Shrink the prostate over several months (e.g., finasteride, dutasteride). Possible sexual side effects.
-
Combination Therapy: Using both alpha blockers and 5-alpha reductase inhibitors if single therapy is insufficient.
-
Tadalafil (Cialis): Can improve urinary symptoms and erectile dysfunction.
2. Minimally Invasive Procedures & Surgery
Procedures may be needed if medications fail or complications arise. Options include:
-
Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP): Removes inner prostate tissue.
-
Transurethral Incision of the Prostate (TUIP): Small cuts in the prostate to improve urine flow.
-
Transurethral Microwave Therapy (TUMT): Uses microwave energy to shrink prostate tissue.
-
Laser Therapy: High-energy lasers destroy or remove excess tissue (PVP, HoLEP).
-
Prostate Lift: Compresses the prostate to ease urine flow with fewer sexual side effects.
-
Water Vapor Thermal Therapy (WVTT): Uses steam to remove excess tissue.
-
Robotic Waterjet Treatment: Water jets remove obstructive tissue.
-
Open or Robot-Assisted Prostatectomy: Surgical removal for very large prostates.
-
Prostate Artery Embolization (PAE): Blocks blood flow to shrink the prostate; performed by a trained interventional radiologist.
Potential Side Effects:
-
Retrograde ejaculation
-
Urinary leakage
-
Urinary tract infection
-
Bleeding
-
Erectile dysfunction
Advertisement