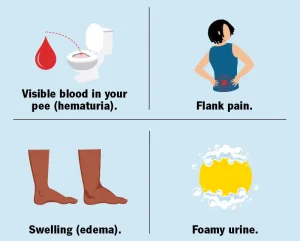
Overview
Diagnosis
IgA nephropathy is often discovered after noticing blood in the urine or during a routine urine test showing blood or protein. Additional exams help confirm the condition and assess kidney function.
Tests used in diagnosis include:
-
Urine tests
A urine sample is checked under a microscope to evaluate how well the kidneys are working and to measure protein levels. Blood in the urine or signs of inflammation in the kidney filters, called glomeruli, may be found. -
Blood tests
These tests can show elevated levels of creatinine or cystatin C, which may indicate kidney disease or reduced kidney function. -
Kidney biopsy
This is the only way to confirm IgA nephropathy. A special needle removes small pieces of kidney tissue that are examined under a microscope. -
Iothalamate clearance test
This test uses a contrast agent to measure how well the kidneys are filtering waste products.
Treatment
There is no cure for IgA nephropathy, and the progression of the disease varies from person to person. Some people require only regular monitoring, while others may need medicines to slow the disease and manage symptoms.
Medicines used in treatment include:
-
High blood pressure drugs
ACE inhibitors and ARBs can lower blood pressure and reduce protein loss in the urine. -
Immunosuppressant medicines
These include corticosteroids and other medicines that calm the immune system, helping prevent immune proteins from damaging the glomeruli. They can cause side effects such as high blood pressure, high blood sugar and increased infection risk. Many newer treatments are available or being tested in clinical trials. -
Omega-3 fatty acids
These may help reduce inflammation in the kidneys. Prescription-strength fish oil supplements may be recommended instead of over-the-counter products. -
Cholesterol medicines
These help manage high cholesterol and may slow the progression of kidney damage. -
Diuretics
These help manage swelling, especially in the hands and feet.
The overall goal of treatment is to protect kidney function and delay or avoid the need for dialysis or a kidney transplant. These options can be lifesaving if kidney function declines severely.
Advertisement