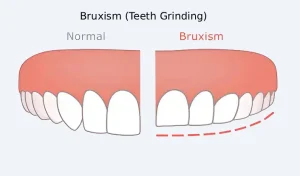
Overview
Diagnosis of Bruxism
A dentist or healthcare provider usually diagnoses bruxism based on:
-
Physical Exam – Checking for tooth wear, jaw tenderness, and muscle soreness
-
Dental X-rays – To assess tooth damage or jawbone changes
-
Sleep Study – Sometimes recommended if sleep bruxism is suspected
-
Medical History – Including stress, medications, or other sleep disorders
Treatment for Bruxism
Treatment focuses on reducing symptoms, preventing tooth damage, and managing underlying causes:
-
Mouthguards or Splints – Custom-fitted devices worn at night to protect teeth
-
Stress Management – Relaxation techniques, yoga, meditation, or counseling
-
Behavioral Therapy – Helps reduce awake bruxism through habit awareness
-
Medications – Muscle relaxants, anti-anxiety drugs, or Botox in severe cases
-
Dental Corrections – Adjusting teeth alignment to reduce grinding
-
Lifestyle Changes – Limiting alcohol, caffeine, and avoiding chewing gum
Complications of Untreated Bruxism
If bruxism is not managed, it can lead to:
-
Severe tooth damage or tooth loss
-
Jaw disorders, including TMJ (temporomandibular joint disorder)
-
Chronic headaches and facial pain
-
Sleep disruption for the patient or partner
-
Increased stress and fatigue
Prevention Tips for Bruxism
-
Manage Stress Effectively – Meditation, breathing exercises, or therapy
-
Avoid Stimulants – Limit caffeine, alcohol, and nicotine, especially before bed
-
Practice Good Sleep Hygiene – Maintain a regular sleep schedule
-
Jaw Exercises and Relaxation – Gentle jaw stretching and massages
-
Use a Night Guard – Especially if prone to sleep bruxism
Key Takeaways:
Bruxism can significantly affect oral health and quality of life. Early diagnosis, protective devices, stress management, and lifestyle changes can help prevent long-term damage and reduce symptoms.
Advertisement