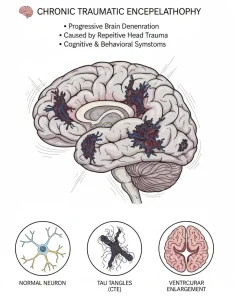
Overview
Diagnosis
Currently, there is no way to definitively diagnose chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) during life. Experts have established clinical guidelines for a related condition called traumatic encephalopathy syndrome (TES). This syndrome describes a group of symptoms that tend to occur together and are linked to CTE.
Healthcare professionals may suspect CTE if a person meets the criteria for TES and has a history of repeated head injuries over many years, often related to contact sports or military service. A confirmed diagnosis of CTE requires evidence of brain tissue degeneration and deposits of abnormal tau and other proteins, which can only be seen during an autopsy after death.
Researchers are working to develop ways to detect CTE in living individuals. Current studies explore the use of neuropsychological tests, advanced brain imaging such as specialized MRI, and biomarkers that could help identify the disease before death.
Treatment
There is no cure for chronic traumatic encephalopathy, and symptoms tend to worsen over time. The main approach focuses on prevention by reducing the risk of repeated head injuries.
For those already affected, treatment aims to manage symptoms and improve quality of life. This may include:
• Education and awareness – Learning how to recognize and manage head injuries to prevent further brain damage.
• Therapy and counseling – Cognitive behavioral therapy can help manage mood changes, depression, and anxiety.
• Medications – Certain medicines may be prescribed to help with depression, anxiety, and behavioral symptoms.
Continued research is needed to better understand CTE and to develop effective treatments that can slow or stop its progression.
Advertisement