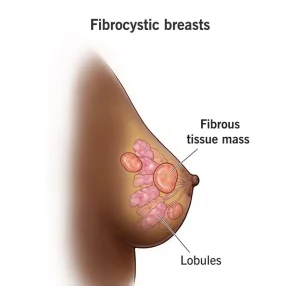
Overview
Diagnosis
To diagnose fibrocystic breast changes, your healthcare provider may recommend a series of evaluations to rule out other conditions and confirm the cause of breast discomfort or lumps.
Clinical breast exam
Your doctor will feel your breasts and nearby lymph nodes in the underarm and lower neck areas to check for unusual tissue or lumps.
-
If the exam and your medical history suggest typical fibrocystic changes, you may not need further testing.
-
If a new lump or suspicious area is found, you may be asked to return after your menstrual period for another exam.
-
If the lump persists or feels abnormal, your provider may recommend imaging tests.
Mammogram
If your doctor detects a lump or thickened area in your breast, a diagnostic mammogram may be ordered. This type of X-ray focuses on the specific area of concern to help identify abnormal tissue.
Ultrasound
An ultrasound uses sound waves to create images of your breast tissue. It’s often performed alongside a mammogram, or used alone for people under 30. Ultrasound helps distinguish between a solid mass and a fluid-filled cyst and is more effective for younger individuals with dense breast tissue.
Fine-needle aspiration
If a breast lump feels like a cyst, your doctor may perform a fine-needle aspiration to withdraw fluid. This simple office procedure can confirm whether the lump is a cyst and may collapse it, relieving pain and pressure.
Breast biopsy
If imaging results are unclear or a solid mass is suspected, a breast biopsy may be performed. During this procedure, a small sample of breast tissue is removed for microscopic analysis.
-
An ultrasound-guided biopsy may be used to locate the lump precisely.
-
A stereotactic biopsy uses mammography to target the area of concern.
Always report new or persistent breast changes to your healthcare provider, even if your last mammogram was normal. Follow-up testing with ultrasound or mammography may be necessary.
Treatment
If fibrocystic breast changes cause no or mild symptoms, treatment may not be needed. However, if pain or large, uncomfortable cysts develop, several treatment options are available.
Treatment for breast cysts
-
Fine-needle aspiration: A thin needle is used to drain fluid from a cyst, which both confirms the diagnosis and relieves discomfort by collapsing the cyst.
-
Surgical excision: In rare cases, surgery may be needed to remove a persistent or recurrent cyst-like lump, especially if it shows worrisome features on examination.
Treatment for breast pain
-
Over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen may ease discomfort.
-
Prescription medication may be used for severe pain.
-
Oral contraceptives may help by stabilizing hormone levels that contribute to fibrocystic breast changes.
These management strategies can reduce symptoms and help maintain breast comfort. Regular monitoring and communication with your healthcare provider are important for ongoing breast health.
Advertisement