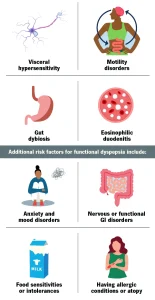
Overview
Diagnosis
A healthcare professional will usually begin with a review of symptoms and a physical examination. To identify the cause of discomfort and rule out other conditions, several diagnostic tests may be recommended.
Blood tests
Blood tests help rule out other medical conditions that can produce symptoms similar to functional dyspepsia.
Tests for Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori)
H. pylori is a bacterium that can cause stomach inflammation and ulcers. Testing for H. pylori may include:
-
A stool sample test
-
A breath test
-
Tissue samples collected during an upper endoscopy
Endoscopy
An upper endoscopy involves using a small camera on a flexible tube to visually examine the upper digestive tract. This allows healthcare professionals to detect inflammation, ulcers, or infection and collect tissue samples if necessary.
In some cases, additional tests may be conducted to check how effectively the stomach empties its contents.
Treatment
If lifestyle changes do not adequately control functional dyspepsia, treatment may involve medication and behavioral therapy. The approach depends on individual symptoms and underlying causes.
Medicines
Various medications may be prescribed to help manage discomfort and improve digestive function:
-
Gas-relieving remedies containing simethicone, such as Mylanta or Gas-X, can help reduce intestinal gas.
-
H-2 receptor blockers like cimetidine (Tagamet HB), famotidine (Pepcid AC), and nizatidine (Axid AR) help lower stomach acid levels.
-
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) such as lansoprazole (Prevacid 24HR), omeprazole (Prilosec OTC), and esomeprazole (Nexium 24HR) block acid production more effectively.
-
Antibiotics may be used when H. pylori infection is detected, often in combination with acid-reducing medication.
-
Low-dose antidepressants, including tricyclic antidepressants and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), can help manage pain signals in the digestive system.
-
Prokinetic drugs help the stomach empty more efficiently and improve the function of the valve between the stomach and esophagus.
-
Anti-emetic medications such as promethazine, prochlorperazine, and meclizine can help control nausea.
Behavior therapy
When medication alone does not relieve symptoms, working with a counselor or therapist may be beneficial. Behavioral therapy can include relaxation techniques, stress management strategies, and coping methods to reduce the impact of digestive discomfort.
This combined medical and behavioral approach helps improve symptom control and enhances quality of life for individuals with functional dyspepsia.
Advertisement