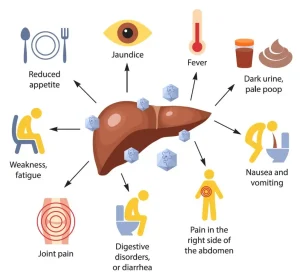
Overview
Diagnosis
Hepatitis A is typically diagnosed through blood tests that detect the presence of the hepatitis A virus in the body. A healthcare professional will take a blood sample, usually from a vein in the arm, and send it to a laboratory for testing. These tests help confirm whether hepatitis A is the cause of the symptoms.
In addition to general blood tests, specific liver function tests may be performed to assess the extent of liver involvement. These include:
-
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) test: Measures the level of ALT, an enzyme found in the liver that is released into the blood when the liver is damaged.
-
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) test: Assesses the presence of liver or bile duct issues.
-
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) test: Measures the level of AST, another enzyme that rises in response to liver injury.
These tests help healthcare professionals determine how well the liver is functioning and monitor the progress of the disease.
Treatment
There is no specific antiviral treatment for hepatitis A. The virus typically resolves on its own as the body clears the infection. In most cases, the liver heals within six months without any lasting damage. The goal of treatment is to manage symptoms and help the body recover.
Supportive Care
To help relieve symptoms and aid in recovery, individuals with hepatitis A may be advised to:
-
Rest: Fatigue is common, and adequate rest is essential to help the body heal.
-
Stay hydrated and eat a balanced diet: Drink plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration, especially if vomiting or diarrhea occurs. While nausea may make eating difficult, try snacking throughout the day and consume high-calorie foods like fruit juice or milk to ensure adequate nutrition.
-
Avoid alcohol: Alcohol can further damage the liver, so it is crucial to avoid it while recovering from hepatitis A.
-
Use medications cautiously: Since the liver may have difficulty processing medications during the infection, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before taking any medications, including over-the-counter drugs.
In most cases, hepatitis A resolves without complications, and the liver recovers fully within several months. However, it is important to follow healthcare guidance to manage symptoms and avoid any potential risks to liver health during the recovery process.
Advertisement