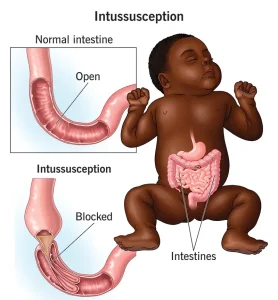
Overview
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of intussusception begins with a medical history and a discussion about when symptoms started. During a physical exam, a healthcare professional may feel a sausage-shaped lump in the abdomen. Imaging tests are essential to confirm the condition. These may include:
-
Ultrasound
-
Abdominal X-ray
-
CT scan
These imaging tests often reveal a bull’s-eye appearance, which indicates that the intestine has folded into itself. Imaging can also show whether a perforation, or tear, has occurred in the intestine.
Treatment
Intussusception is treated as a medical emergency to prevent dehydration, shock and infection. Treatment depends on the severity of the condition and whether complications are present.
Common treatment options include:
-
A water-soluble contrast or air enema, which works as both a diagnostic and therapeutic procedure. This method is successful in most children unless a perforation is present.
-
Surgery when the intestine is torn, when an enema is unsuccessful or when a lead point is causing the condition. Surgery frees the trapped intestine, removes the blockage and addresses any dead tissue. It is also the primary treatment in adults.
In some cases, intussusception resolves on its own without treatment.
Advertisement