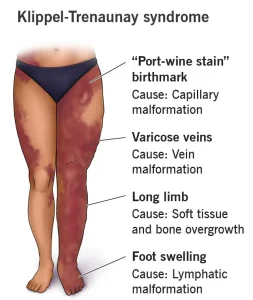
Overview
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of Klippel-Trenaunay syndrome begins with a physical exam and a detailed review of symptoms. Referral to a vascular malformations specialist is often recommended for a thorough evaluation and guidance on treatment options. During the assessment, the healthcare provider typically:
-
Asks questions about family and medical history
-
Examines the affected areas for swelling, varicose veins, and port-wine stains
-
Visually evaluates overgrowth of bones and soft tissues
Several diagnostic tests may be used to identify the type and severity of the condition and assist in planning treatment. These may include:
-
Duplex ultrasound scanning, which uses high-frequency sound waves to create detailed images of blood vessels and blood flow
-
MRI and magnetic resonance angiography to identify soft tissue and blood vessel malformations
-
Scanogram to create X-ray images that help measure bone length
-
CT scan or CT angiography to produce 3D images and reveal blood clots
-
Contrast venography to highlight atypical veins, blockages, or clots
-
Coagulation studies to evaluate how well blood clots
-
Genetic studies to check for gene differences that may explain why the condition developed
Treatment
Although there is no cure for Klippel-Trenaunay syndrome, treatment focuses on managing symptoms and preventing complications. Because the condition can affect multiple systems in the body, care is often provided by a team of specialists, which may include experts in vascular medicine and surgery, dermatology, interventional radiology, orthopedics, rehabilitation, and physical therapy.
Treatment plans are tailored to each person’s needs and may include:
-
Compression therapy using bandages, elastic garments, or pneumatic compression devices to help reduce swelling, varicose vein issues, and skin ulcers
-
Skin care routines to reduce the risk of infection and manage superficial bleeding
-
Physical therapy that may include massage, compression, and guided exercises to relieve lymphedema and swelling
-
Orthopedic devices such as specialized shoes or inserts to correct leg length differences
-
Epiphysiodesis, an orthopedic surgical procedure used to control excessive growth of the lower limb
-
Embolization to block blood flow to certain affected vessels
-
Laser therapy to lighten or remove port-wine stains and treat skin blebs
-
Laser or radiofrequency ablation to close off malformed veins
-
MR-guided ablation to treat blood vessels using laser or cautery under MRI guidance
-
Sclerotherapy, in which a solution is injected into a vein to create scar tissue that helps close it
-
Surgery to remove or reconstruct affected veins, correct bone overgrowth, or remove excess tissue
-
Medication, including oral or topical treatments, to address vascular and lymphatic malformations, with ongoing monitoring for possible side effects
Additional care may be needed for complications such as bleeding, infection, blood clots, or skin ulcers. Special considerations may also be required during pregnancy to help prevent complications.
Advertisement