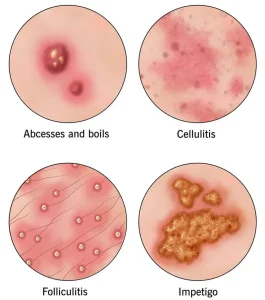
Overview
Diagnosis
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is diagnosed by checking tissue samples or nasal secretions for drug-resistant bacteria. The sample is sent to a laboratory where it is placed in a nutrient-rich dish to encourage bacterial growth. Traditional cultures take about 48 hours to show results, but newer tests can detect staph DNA within hours, allowing for faster diagnosis.
During a physical exam, your doctor will examine any cuts or skin lesions and may take samples of tissue or fluid for testing.
Treatment
MRSA infections, whether healthcare-associated or community-associated, can respond to certain antibiotics.
Treatment options include:
• Draining large boils or abscesses through minor surgery in addition to taking antibiotics
• Antibiotics may not always be necessary for small, shallow abscesses; drainage alone may be sufficient
Treatment plans depend on the location and severity of the infection, and your doctor may refer you to a specialist such as a dermatologist for skin infections or a cardiologist if the heart is affected.
Preparing for your appointment
Before your appointment, it can help to prepare:
• Detailed descriptions of your symptoms
• Information about your past medical problems
• Family medical history
• A list of medications and supplements you take
• Questions you want to ask your doctor
This preparation helps your healthcare provider determine the most effective treatment and whether further testing or specialist care is needed.
Advertisement