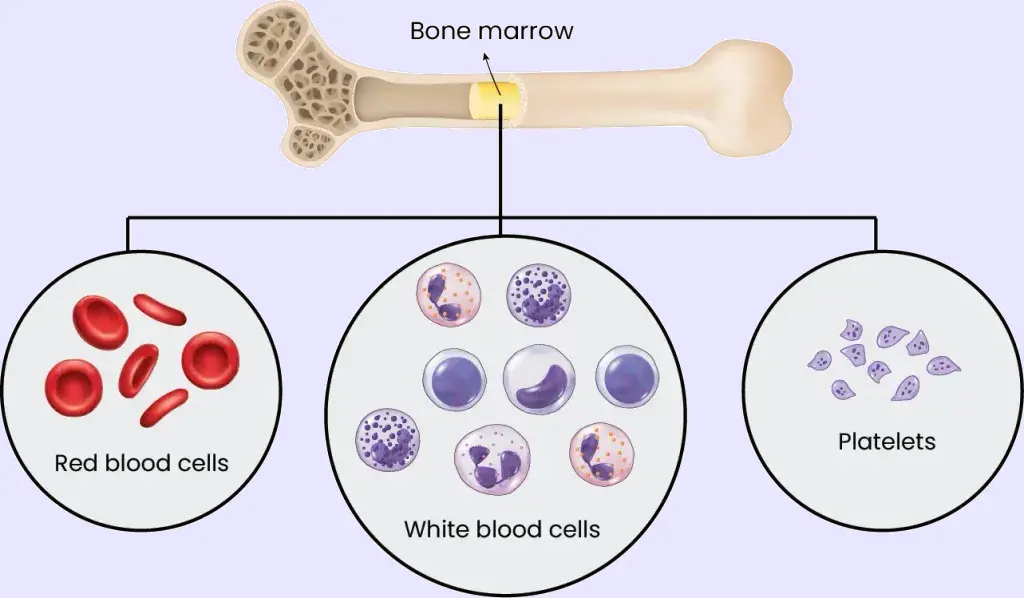
Diagnosis Diagnosis of myelofibrosis usually begins with a physical examination and a review of symptoms. Additional tests are often needed to confirm this type of bone marrow cancer. These may include blood tests, imaging studies, and bone marrow testing. A healthcare professional may examine your abdomen to check for signs of an enlarged spleen or liver, which are common findings …
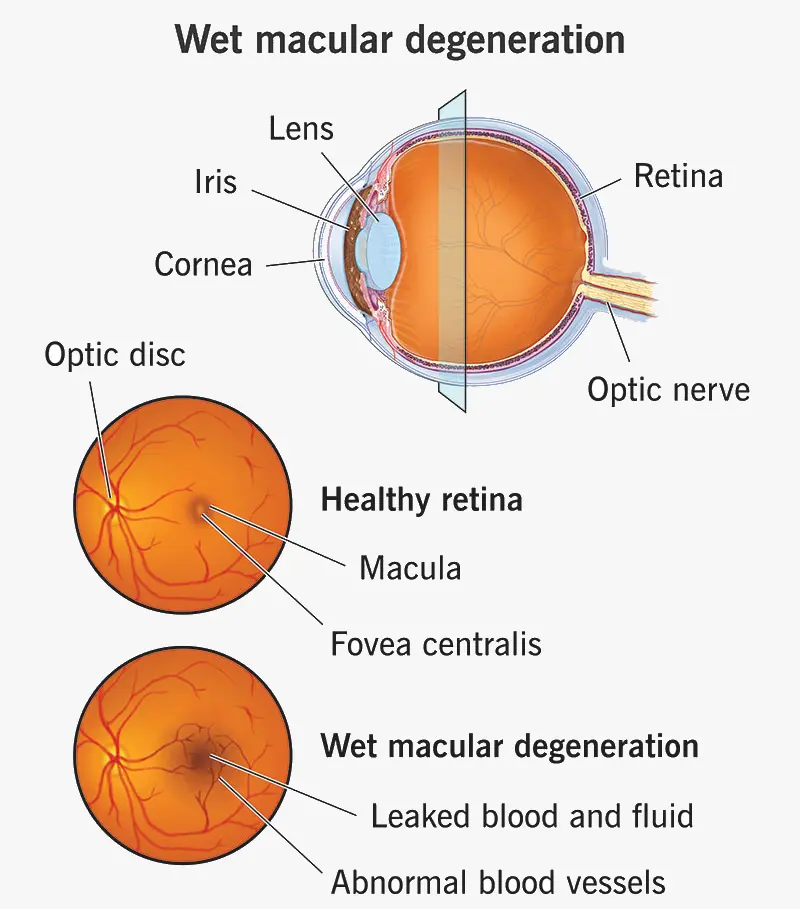
Wet Macular Degeneration
Diagnosis Wet macular degeneration is diagnosed through a comprehensive eye exam and specialized imaging tests that evaluate the retina and macula. Early detection is essential to prevent significant vision loss. A healthcare professional, usually an ophthalmologist, may perform the following: Dilated eye exam: Eye drops are used to widen the pupils, allowing the doctor to examine the retina and macula …
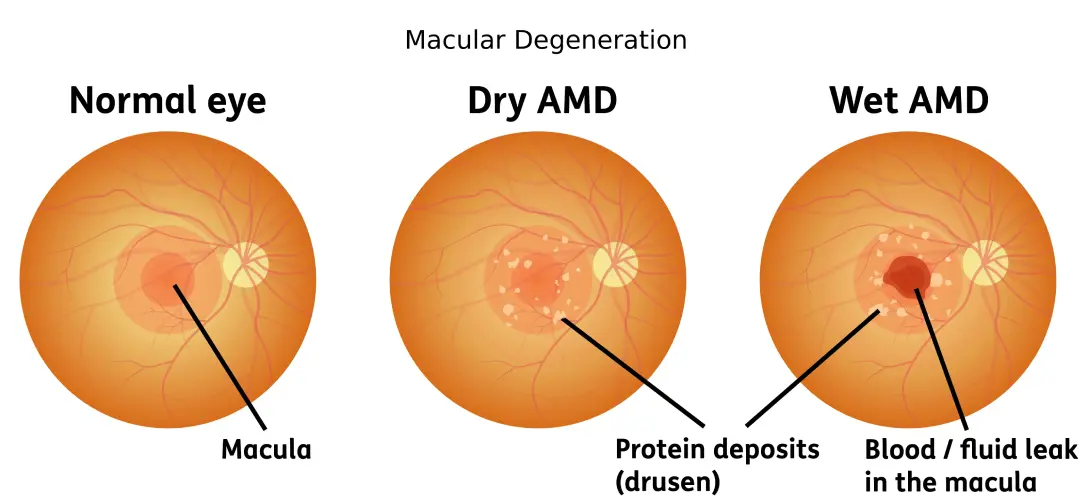
Dry Macular Degeneration
Diagnosis An eye care professional can diagnose dry macular degeneration by reviewing your medical and family history and performing a comprehensive eye exam. Several specialized tests may be used to confirm the diagnosis and determine the stage of the condition. Examination of the back of the eye During this exam, eye drops are used to dilate the pupils. The eye …
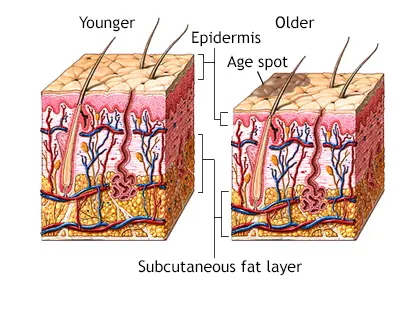
Age Spots (Liver Spots)
Age spots — also called liver spots or solar lentigines — are common skin changes caused by long-term sun exposure. While harmless, they may look similar to other skin conditions, so proper diagnosis is important to ensure the right treatment. Diagnosis of Age Spots Diagnosing age spots typically involves a visual examination and, if needed, a skin biopsy to rule …
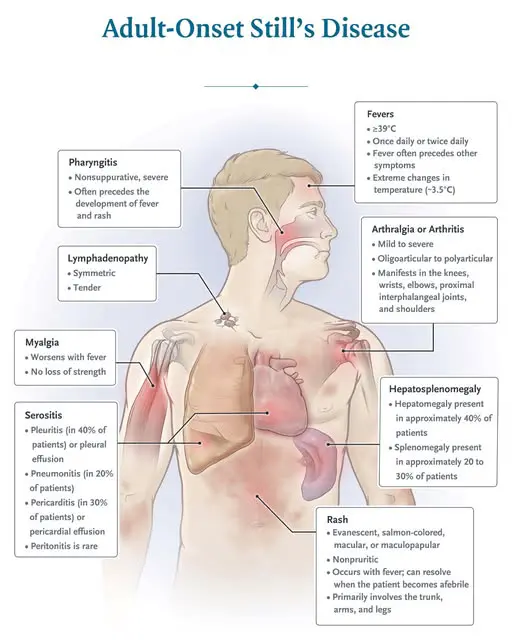
Adult Still Disease
Diagnosis of Adult Still Disease There is no single test that can confirm adult Still disease. Doctors use a combination of approaches: Imaging tests: Reveal joint or tissue damage caused by the disease Blood tests: Help rule out other conditions with similar symptoms, including autoimmune or infectious disorders Related tests may include: Antinuclear antibody (ANA) test C-reactive protein (CRP) test …
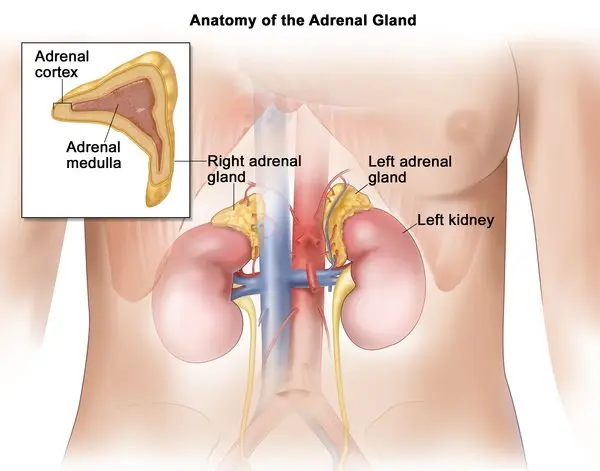
Adrenoleukodystrophy
Diagnosis of ALD Doctors diagnose ALD by evaluating symptoms, medical history, family history, and lab tests. Blood Testing Blood tests are essential for diagnosing ALD: Very long-chain fatty acids (VLCFAs): High levels in the blood indicate ALD Genetic testing: Identifies mutations causing ALD Adrenal gland function: Blood tests can assess how well the adrenal glands are working MRI Magnetic Resonance …
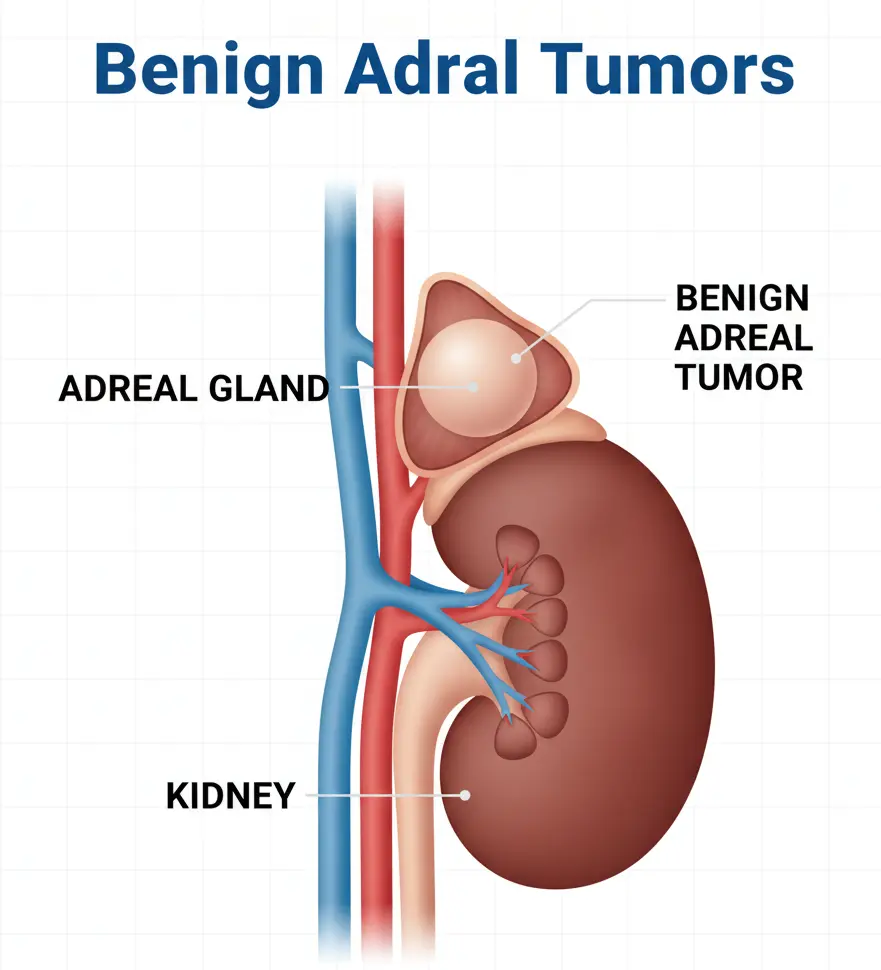
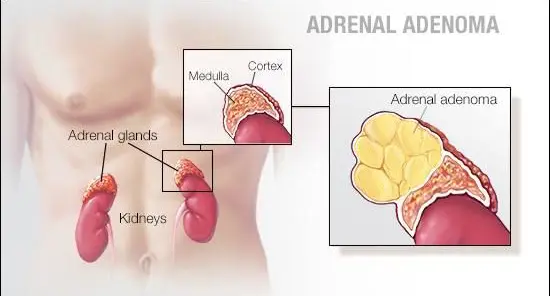
Benign Adrenal Tumors
Diagnosis Benign adrenal tumors are typically found by chance on imaging tests. Once detected, a healthcare professional evaluates: Cancer risk: Determining whether the tumor has characteristics that suggest malignancy. Hormone production: Checking if the tumor secretes excess hormones, which can affect blood pressure, metabolism, and other bodily functions. Diagnostic tests may include: Blood and urine tests: Assess for excess hormones …
Adrenal Cancer
Diagnosis of Adrenal Cancer Healthcare professionals use a combination of physical exams, lab tests, imaging studies, and sometimes surgery to diagnose adrenal cancer. Blood and Urine Tests Lab tests may measure hormone levels produced by the adrenal glands. Hormones commonly tested include: Cortisol Aldosterone Androgens Abnormal levels can indicate the presence of an adrenal tumor or cancer. Imaging Tests Imaging …
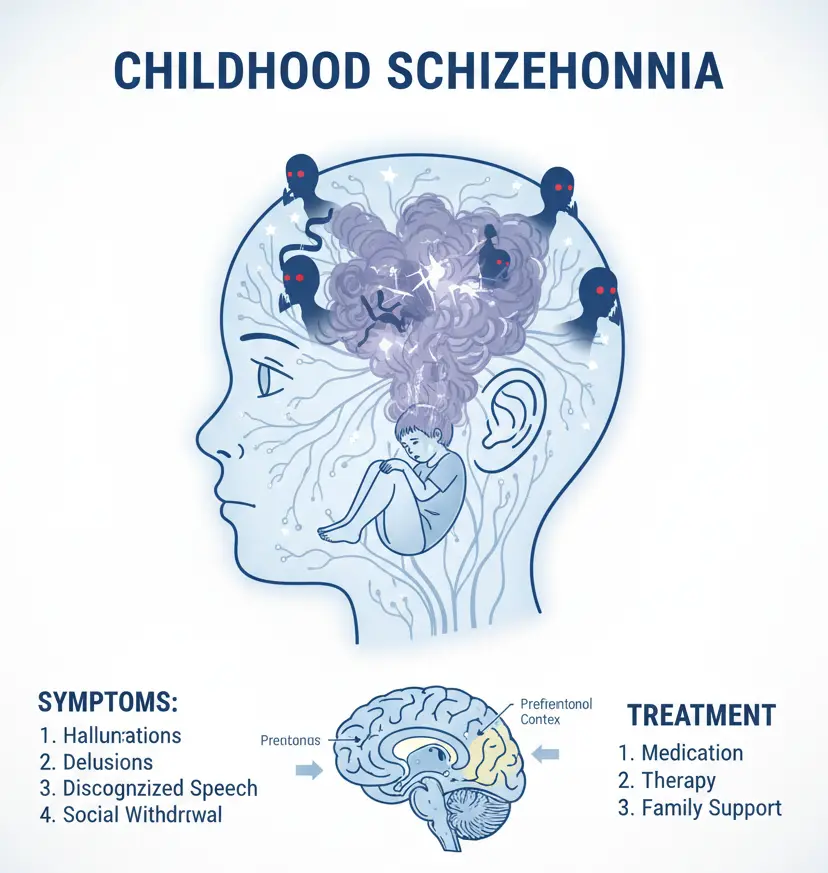
Childhood Schizophrenia
Diagnosis Diagnosis of childhood schizophrenia involves ruling out other mental health disorders and ensuring symptoms are not caused by alcohol, drugs, medication, or a medical condition. The diagnostic process may include: Physical exam to check for other causes or complications Tests and screenings to rule out similar conditions and check for alcohol or drug use Imaging studies such as MRI …
Adnexal Tumors
Diagnosis Healthcare professionals diagnose adnexal tumors or masses through a combination of physical exams, imaging tests, and blood tests. Pelvic Exam During a pelvic exam, a healthcare professional: Inserts gloved fingers into the vagina while pressing a hand on the belly to feel the pelvic organs Examines the external genitals, vagina, and cervix for any abnormalities Imaging Tests Imaging tests …