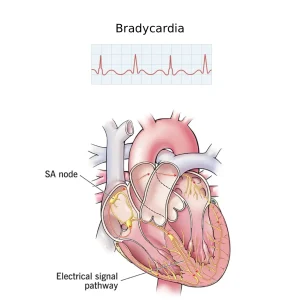
Overview
Bradycardia is a condition in which the heart beats slower than normal, typically fewer than 60 beats per minute in adults. A slow heart rate is not always a problem and can be normal in healthy, physically active individuals. However, when bradycardia prevents the heart from pumping enough oxygen-rich blood to the body, it can cause symptoms and may require medical evaluation and treatment.
Symptoms
Some people with bradycardia may not experience symptoms, especially if the slow heart rate does not affect blood flow. When symptoms occur, they may include the following.
• Fatigue or weakness
• Dizziness or lightheadedness
• Shortness of breath
• Chest pain
• Confusion or difficulty concentrating
• Fainting or near-fainting episodes
• Reduced ability to exercise
Causes
Bradycardia can result from problems with the heart’s electrical system or other underlying conditions.
• Aging-related changes in heart tissue
• Damage to heart tissue from heart disease or a heart attack
• Congenital heart defects present at birth
• Inflammation of heart tissue
• Certain medications, including beta blockers and calcium channel blockers
• Electrolyte imbalances such as abnormal potassium levels
• Hypothyroidism
• Sleep apnea
Risk factors
Several factors can increase the risk of developing bradycardia.
• Older age
• History of heart disease or heart surgery
• High blood pressure
• Smoking
• Excessive alcohol use
• Use of medications that slow heart rate
• Chronic medical conditions such as thyroid disorders
Complications
If bradycardia is severe or untreated, it can lead to serious health problems.
• Frequent fainting or falls
• Heart failure
• Low blood pressure
• Sudden cardiac arrest in severe cases
• Reduced quality of life due to persistent symptoms
Prevention
Not all cases of bradycardia can be prevented, but certain measures may help reduce risk and support heart health.
• Maintain a heart-healthy lifestyle with regular physical activity
• Eat a balanced diet low in saturated fat and salt
• Avoid smoking and limit alcohol intake
• Manage chronic conditions such as high blood pressure and thyroid disorders
• Take medications only as prescribed and review side effects with a healthcare provider
• Seek medical evaluation for unexplained dizziness, fainting, or fatigue
Advertisement