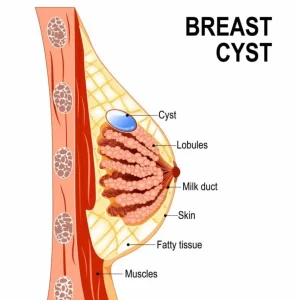
Overview
Breast cysts are fluid-filled sacs within the breast tissue and are a common, benign breast condition. They often occur in women between the ages of 35 and 50 and may develop as part of normal hormonal changes. Breast cysts can vary in size and may feel soft or firm. Although they are not cancerous, they can sometimes cause discomfort and may require evaluation to rule out other conditions.
Symptoms
Breast cysts may cause noticeable changes in the breast, especially before menstruation.
• A smooth, round, or oval lump that moves easily under the skin
• Breast pain or tenderness
• Swelling in one area of the breast
• Lump size that changes with the menstrual cycle
• Discomfort that improves after menstruation
• Rarely, nipple discharge that may be clear or straw-colored
Causes
Breast cysts develop when fluid builds up inside breast glands.
• Hormonal fluctuations related to the menstrual cycle
• Estrogen stimulation of breast tissue
• Blockage of milk ducts
• Normal aging changes in breast tissue
Risk factors
Certain factors may increase the likelihood of developing breast cysts.
• Being between 35 and 50 years of age
• Perimenopause or menopause with hormone therapy
• History of benign breast conditions
• Hormonal imbalance
Complications
Breast cysts usually do not cause serious complications, but some issues may arise.
• Breast pain or persistent discomfort
• Anxiety related to breast lump discovery
• Infection of a cyst in rare cases
• Recurrent cyst formation
Prevention
Breast cysts cannot always be prevented, but some steps may help reduce discomfort and promote breast health.
• Regular breast self-awareness and monitoring
• Wearing a supportive bra to reduce discomfort
• Limiting caffeine if it worsens symptoms
• Managing hormonal balance with medical guidance
• Seeking medical evaluation for new or changing breast lumps
Advertisement