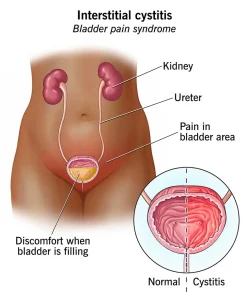
Overview
Cystitis is inflammation of the urinary bladder, most commonly caused by a bacterial infection. It is a type of urinary tract infection and occurs more frequently in women due to anatomical differences. While cystitis is often mild and easily treated, untreated cases can lead to more serious infections involving the kidneys. Cystitis can also occur without infection, triggered by irritation, medications, or underlying health conditions.
Symptoms
Symptoms of cystitis usually involve the urinary system and may develop suddenly.
Common symptoms include:
-
Frequent urge to urinate
-
Burning or pain during urination
-
Passing small amounts of urine frequently
-
Cloudy, dark, or strong-smelling urine
-
Lower abdominal or pelvic discomfort
-
Blood in the urine
-
Low-grade fever in some cases
-
General feeling of unwellness
In older adults, symptoms may be less specific.
Causes
Cystitis most often occurs when bacteria enter the urinary tract and multiply in the bladder.
Common causes include:
-
Bacterial infection, especially Escherichia coli
-
Sexual activity introducing bacteria into the urethra
-
Use of urinary catheters
-
Irritation from personal hygiene products
-
Certain medications or radiation therapy
-
Conditions that prevent complete bladder emptying
Noninfectious cystitis may occur due to chemical or physical irritation.
Risk factors
Certain factors increase the likelihood of developing cystitis.
Risk factors include:
-
Female anatomy with a shorter urethra
-
Sexual activity
-
Pregnancy
-
Menopause
-
Diabetes
-
Use of urinary catheters
-
Enlarged prostate in men
These factors can make bladder infections more likely.
Complications
If cystitis is not properly treated, complications may occur.
Possible complications include:
-
Recurrent urinary tract infections
-
Kidney infection if bacteria spread upward
-
Chronic bladder inflammation
-
Blood in the urine
-
Reduced quality of life due to frequent symptoms
Prompt treatment usually prevents serious complications.
Prevention
Several measures can help reduce the risk of cystitis.
Preventive strategies include:
-
Drinking plenty of fluids
-
Urinating regularly and after sexual activity
-
Wiping from front to back after using the toilet
-
Avoiding irritating feminine hygiene products
-
Managing underlying conditions such as diabetes
-
Following medical advice for recurrent infections
Good hygiene and early treatment are key to preventing complications of cystitis.
Advertisement