Overview
Dengue fever is a mosquito-borne viral illness caused by the dengue virus and transmitted primarily by Aedes mosquitoes. It is common in tropical and subtropical regions and can range from a mild flu-like illness to a severe, life-threatening condition. Early recognition and appropriate medical care are important to reduce complications.
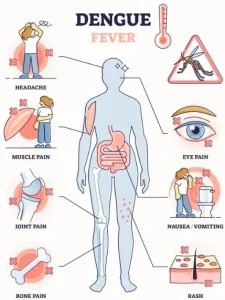
Symptoms
Symptoms usually appear 4 to 10 days after being bitten by an infected mosquito and may include:
-
Sudden high fever
-
Severe headache
-
Pain behind the eyes
-
Muscle and joint pain
-
Nausea or vomiting
-
Skin rash
-
Fatigue and weakness
-
Mild bleeding such as nose or gum bleeding
Causes
Dengue fever is caused by infection with one of the four types of dengue virus:
-
Bite from an infected Aedes mosquito
-
Exposure in areas with active dengue transmission
-
Previous infection with a different dengue virus type, which may increase severity
Risk Factors
Certain factors increase the risk of contracting dengue fever:
-
Living in or traveling to tropical or subtropical regions
-
Poor mosquito control measures
-
Stagnant water around living areas
-
Lack of protective clothing or mosquito repellents
-
Previous dengue infection
Complications
In some cases, dengue fever can progress to severe dengue:
-
Dengue hemorrhagic fever
-
Dengue shock syndrome
-
Severe bleeding
-
Plasma leakage leading to fluid accumulation
-
Organ damage
-
Low platelet count
Prevention
Preventive measures focus on avoiding mosquito bites and controlling mosquito populations:
-
Using mosquito repellents
-
Wearing long-sleeved clothing
-
Sleeping under mosquito nets
-
Eliminating standing water where mosquitoes breed
-
Using window screens and insecticides
-
Community-based mosquito control programs
Advertisement