Overview
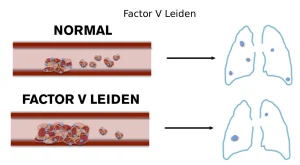
Factor V Leiden is a genetic blood clotting disorder that increases the risk of developing abnormal blood clots, especially in the veins. It is caused by a mutation in the factor V gene, which makes the clotting protein resistant to being broken down by activated protein C. As a result, blood clots can form more easily than normal.
Many people with Factor V Leiden never develop symptoms, but the condition is a leading inherited cause of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. The disorder can be inherited from one parent or both, affecting the level of risk.
Symptoms
Factor V Leiden itself usually does not cause symptoms unless a blood clot develops. Symptoms depend on the location of the clot.
Common symptoms of deep vein thrombosis include:
-
Swelling in one leg or arm
-
Pain or tenderness, often starting in the calf
-
Warmth over the affected area
-
Red or discolored skin
Symptoms of pulmonary embolism may include:
-
Sudden shortness of breath
-
Chest pain that may worsen with deep breathing
-
Rapid heartbeat
-
Coughing, sometimes with blood
-
Dizziness or fainting
Some individuals may experience recurrent miscarriages or pregnancy complications.
Causes
Factor V Leiden is caused by a specific genetic mutation in the F5 gene. This mutation alters the structure of factor V, making it resistant to normal regulation by activated protein C.
The condition is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern:
-
Having one copy of the mutated gene increases clotting risk moderately
-
Having two copies significantly increases the risk of serious blood clots
The mutation is most commonly found in people of European descent.
Risk Factors
While the mutation itself increases clotting risk, certain factors can further raise the chance of developing blood clots:
-
Family history of blood clots
-
Prolonged immobility, such as long flights or bed rest
-
Surgery or physical trauma
-
Pregnancy and the postpartum period
-
Use of estrogen-containing birth control pills or hormone therapy
-
Obesity
-
Smoking
The combination of Factor V Leiden with these risk factors greatly increases clot formation risk.
Complications
Factor V Leiden can lead to serious and potentially life-threatening complications, including:
-
Deep vein thrombosis
-
Pulmonary embolism
-
Recurrent blood clots
-
Chronic leg pain or swelling due to post-thrombotic syndrome
-
Pregnancy complications such as miscarriage, preeclampsia, or placental abruption
Early diagnosis and proper management can significantly reduce the risk of complications.
Prevention
Factor V Leiden cannot be prevented because it is inherited, but complications can often be reduced through preventive measures:
-
Avoiding prolonged periods of immobility
-
Staying well hydrated
-
Maintaining a healthy weight
-
Avoiding smoking
-
Discussing hormone use with a healthcare provider
-
Using preventive blood-thinning medications during high-risk situations such as surgery or pregnancy
Regular medical follow-up and awareness of clot symptoms are essential for reducing long-term risks associated with Factor V Leiden.
Advertisement