Overview
Female infertility is the inability to become pregnant after one year of regular, unprotected sexual intercourse, or after six months for women over the age of 35. It can result from problems with ovulation, the fallopian tubes, the uterus, or hormonal balance. Female infertility may occur on its own or in combination with male infertility factors. Advances in medical evaluation and treatment have improved the chances of conception for many women.
Symptoms
The main symptom of female infertility is difficulty becoming pregnant. Other symptoms may suggest an underlying cause:
-
Irregular or absent menstrual periods
-
Very heavy or very light menstrual bleeding
-
Pelvic pain, especially during menstruation or intercourse
-
Hormonal symptoms such as acne or excess facial hair
-
Painful periods
Some women have no noticeable symptoms aside from infertility.
Causes
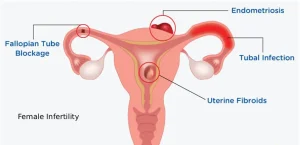
Female infertility can be caused by a wide range of medical and structural issues:
-
Ovulation disorders that affect the release of eggs
-
Blocked or damaged fallopian tubes
-
Uterine abnormalities such as fibroids or polyps
-
Endometriosis
-
Hormonal imbalances affecting the menstrual cycle
-
Primary ovarian insufficiency
-
Chronic medical conditions or infections
Often, more than one factor contributes to infertility.
Risk Factors
Several factors increase the risk of female infertility:
-
Increasing age, especially after age 35
-
Irregular menstrual cycles
-
Smoking, excessive alcohol use, or drug use
-
Obesity or being underweight
-
Chronic stress
-
Sexually transmitted infections
-
Previous pelvic surgery or cancer treatment
Lifestyle and medical history play an important role in fertility.
Complications
Female infertility can be associated with physical and emotional complications:
-
Emotional distress, anxiety, or depression
-
Relationship stress
-
Increased risk of pregnancy complications with advanced age
-
Side effects from fertility treatments
-
Financial strain related to prolonged treatment
Psychological support is often an important part of infertility care.
Prevention
Not all causes of female infertility can be prevented, but certain steps may help protect fertility:
-
Maintaining a healthy body weight
-
Avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol intake
-
Practicing safe sex to prevent infections
-
Managing chronic medical conditions early
-
Seeking medical advice for irregular or absent periods
-
Avoiding unnecessary exposure to toxins or radiation
Early evaluation and healthy lifestyle choices can help reduce the risk of female infertility and improve reproductive health.
Advertisement