Overview
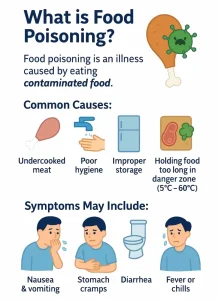
Food poisoning is an illness caused by consuming contaminated food or beverages. It occurs when harmful bacteria, viruses, parasites, or toxins enter the body through food. Symptoms often develop suddenly and can range from mild gastrointestinal discomfort to severe illness requiring medical care. Most cases resolve within a few days, but some may lead to serious complications, especially in vulnerable individuals.
Symptoms
Symptoms of food poisoning vary depending on the contaminant and amount ingested:
-
Nausea and vomiting
-
Diarrhea, which may be watery or bloody
-
Abdominal cramps or pain
-
Fever
-
Headache
-
Fatigue or weakness
-
Dehydration due to fluid loss
Symptoms can appear within hours or days after consuming contaminated food.
Causes
Food poisoning is caused by eating food or drinking liquids contaminated during production, handling, or storage. Common causes include:
-
Bacteria such as Salmonella, E. coli, and Campylobacter
-
Viruses such as norovirus
-
Parasites such as Giardia
-
Toxins produced by bacteria
-
Improper food handling or storage
-
Consumption of undercooked or raw foods
Poor hygiene practices increase the risk of contamination.
Risk Factors
Certain individuals are at higher risk of severe food poisoning:
-
Young children
-
Older adults
-
Pregnant individuals
-
People with weakened immune systems
-
Chronic medical conditions
Risk also increases with consumption of high-risk foods and poor food safety practices.
Complications
While most people recover fully, food poisoning can sometimes cause complications:
-
Severe dehydration
-
Electrolyte imbalances
-
Kidney failure in certain infections
-
Reactive arthritis
-
Bloodstream infections in severe cases
Prompt treatment reduces the risk of serious complications.
Prevention
Food poisoning can often be prevented by following safe food practices:
-
Washing hands before handling food
-
Cooking foods thoroughly
-
Storing foods at proper temperatures
-
Avoiding cross-contamination between raw and cooked foods
-
Drinking safe, clean water
-
Avoiding food from unsafe or unhygienic sources
Good food safety habits are key to preventing food poisoning and protecting overall health.
Advertisement