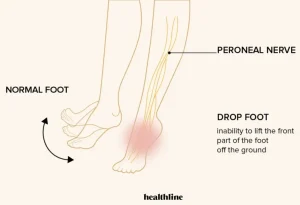
Overview
Foot drop is a condition characterized by difficulty lifting the front part of the foot, leading to dragging of the toes while walking. It is not a disease itself but a sign of an underlying neurological, muscular, or anatomical problem. People with foot drop often adopt a high-stepping gait to prevent the toes from catching on the ground. The condition can affect one or both feet and may be temporary or permanent depending on the cause.
Symptoms
Symptoms of foot drop vary in severity and may include:
-
Difficulty lifting the front part of the foot
-
Dragging of toes while walking
-
High-stepping or slapping gait
-
Numbness or tingling in the foot or toes
-
Weakness in the ankle or lower leg
-
Frequent tripping or falling
Symptoms may worsen with prolonged walking or standing.
Causes
Foot drop occurs due to weakness or paralysis of the muscles responsible for lifting the foot, often caused by nerve damage. Common causes include:
-
Injury or compression of the peroneal nerve
-
Herniated spinal disc
-
Stroke
-
Multiple sclerosis
-
Diabetes-related nerve damage
-
Muscle disorders such as muscular dystrophy
-
Brain or spinal cord injury
Identifying the underlying cause is essential for proper management.
Risk Factors
Factors that increase the risk of developing foot drop include:
-
Prolonged kneeling or squatting
-
Wearing tight casts or braces around the knee
-
Diabetes or other conditions causing nerve damage
-
History of stroke or neurological disease
-
Spinal disorders or injuries
Occupational or repetitive movements may also contribute.
Complications
If untreated, foot drop can lead to several complications:
-
Increased risk of falls and injuries
-
Difficulty walking or climbing stairs
-
Muscle tightening or contractures
-
Reduced mobility and independence
-
Changes in posture or gait-related pain
Early intervention helps minimize long-term complications.
Prevention
Foot drop cannot always be prevented, but certain measures may reduce risk:
-
Managing chronic conditions such as diabetes
-
Avoiding prolonged pressure on the knees or legs
-
Using proper protective equipment during activities
-
Seeking early treatment for nerve or muscle injuries
-
Maintaining strength and flexibility through appropriate exercises
Prompt evaluation of walking difficulties can help identify causes early and improve outcomes.
Advertisement