Overview
Gingivitis is a common and mild form of gum disease that causes inflammation of the gums surrounding the teeth. It occurs when plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, builds up on the teeth and along the gumline. Gingivitis is usually reversible with proper oral hygiene and early treatment. If left untreated, it can progress to more serious forms of gum disease that may lead to tooth loss.
Symptoms
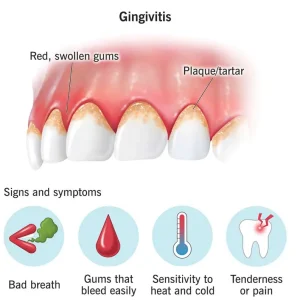
Symptoms of gingivitis are often mild in the early stages but may become more noticeable over time. Common symptoms include:
-
Red or swollen gums
-
Bleeding gums, especially during brushing or flossing
-
Tender or sore gums
-
Bad breath that does not go away
-
Receding gums in some cases
Pain is usually minimal, which is why gingivitis may go unnoticed without regular dental checkups.
Causes
Gingivitis is primarily caused by poor oral hygiene that allows plaque to accumulate on the teeth and gums. Common causes include:
-
Inadequate brushing and flossing
-
Plaque buildup along the gumline
-
Hormonal changes, such as during pregnancy or puberty
-
Smoking or tobacco use
-
Ill-fitting dental appliances
-
Certain medications that reduce saliva flow
Bacteria in plaque trigger inflammation of the gums.
Risk Factors
Several factors increase the risk of developing gingivitis, including:
-
Poor oral hygiene habits
-
Smoking or chewing tobacco
-
Diabetes
-
Poor nutrition, especially vitamin C deficiency
-
Older age
-
Hormonal changes
-
Weakened immune system
These factors can make gums more vulnerable to infection and inflammation.
Complications
If gingivitis is not treated, it can lead to more serious oral health problems. Possible complications include:
-
Progression to periodontitis
-
Gum recession
-
Tooth loosening or tooth loss
-
Increased risk of systemic health issues linked to gum disease
Early treatment helps prevent permanent damage to the gums and teeth.
Prevention
Gingivitis can usually be prevented with good oral care practices:
-
Brushing teeth at least twice a day
-
Flossing daily to remove plaque between teeth
-
Using an antiseptic mouthwash if recommended
-
Avoiding tobacco products
-
Eating a balanced diet to support gum health
-
Scheduling regular dental checkups and cleanings
Consistent oral hygiene and routine dental care are key to preventing gingivitis and maintaining healthy gums.
Advertisement