Overview
Heavy menstrual bleeding, also known as menorrhagia, is a condition in which menstrual periods involve excessive blood loss or last longer than normal. It can interfere with daily activities, work, and quality of life. While occasional heavy periods may occur, persistent heavy menstrual bleeding often indicates an underlying medical or hormonal issue and may require medical evaluation.
Symptoms
Symptoms of heavy menstrual bleeding may vary in severity and duration.
Common symptoms include:
-
Menstrual bleeding lasting longer than seven days
-
Needing to change sanitary pads or tampons every one to two hours
-
Passing large blood clots during menstruation
-
Needing to use double sanitary protection
-
Bleeding through clothing or bedding
-
Fatigue or weakness due to blood loss
-
Shortness of breath in cases of anemia
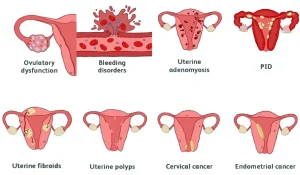
Causes
Heavy menstrual bleeding can result from hormonal, structural, or medical conditions.
Common causes include:
-
Hormonal imbalance affecting ovulation
-
Uterine fibroids
-
Uterine polyps
-
Adenomyosis
-
Bleeding disorders
-
Intrauterine devices without hormones
-
Certain medications, including blood thinners
-
Complications related to pregnancy
Risk Factors
Certain factors increase the likelihood of heavy menstrual bleeding.
Risk factors include:
-
Adolescence or perimenopause
-
History of irregular menstrual cycles
-
Thyroid disorders
-
Obesity
-
Family history of bleeding disorders
-
Long-term use of certain medications
-
Chronic medical conditions
Complications
If left untreated, heavy menstrual bleeding can lead to significant health problems.
Possible complications include:
-
Iron-deficiency anemia
-
Severe fatigue
-
Reduced physical and emotional well-being
-
Pregnancy complications
-
Need for surgical intervention in severe cases
Prevention
Not all cases of heavy menstrual bleeding can be prevented, but early management can reduce severity and complications.
Preventive measures include:
-
Regular gynecological checkups
-
Tracking menstrual cycles and bleeding patterns
-
Managing underlying hormonal or medical conditions
-
Maintaining a healthy weight
-
Following prescribed treatment plans
-
Seeking medical advice when bleeding patterns change
If you want, I can also add diagnosis methods, treatment options, or lifestyle management sections in the same SEO-friendly, WordPress- and ACF-ready format.
Advertisement